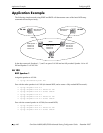
BGP for IPv6 Overview Configuring BGP
page 4-64 OmniSwitch 6800/6850/9000 Advanced Routing Configuration Guide December 2007
BGP for IPv6 Overview
IP version 6 (IPv6) is a new version of the Internet Protocol, designed as the successor to IP version 4
(IPv4), to overcome certain limitations in IPv4. IPv6 adds significant extra features that were not possible
with IPv4. These include automatic configuration of hosts, extensive multicasting capabilities, and built-in
security using authentication headers and encryption. Built-in support for QOS and path control are also
features found in IPv6.
IPv6 is a hierarchical 128-bit addressing scheme that consists of 8 fields, comprising 16 bits each. An IPv6
address is written as a hexadecimal value (0-F) in groups of four, separated by colons. IPv6 provides
3x10^38 addresses, which can help overcome the shortage of IP addresses needed for internet usage.
There are three types of IPv6 addresses: Unicast, Anycast, and Multicast. A Unicast address identifies a
single interface and a packet destined for a Unicast address is delivered to the interface identified by that
address. An Anycast address identifies a set of interfaces and a packet destined for an Anycast address is
delivered to the nearest interface identified by that Anycast address. A Multicast address identifies a set of
interfaces and a packet destined for a Multicast address is delivered to all the interfaces identified by that
Multicast address. There are no broadcast addresses in IPv6.
BGP uses Multiprotocol Extensions to support IPv6. The same procedures used for IPv4 prefixes can be
applied for IPv6 prefixes as well and the exchange of IPv4 prefixes will not be affected by this new
feature. However, there are some attributes that are specific to IPv4, such as AGGREGATOR,
NEXT_HOP and NLRI. Multiprotocol Extensions for BGP also supports backward compatibility for the
routers that do not support this feature. The OmniSwitch implementation supports Multiprotocol BGP as
defined in the following RFCs: 4271, 2439, 3392, 2385, 1997, 4456, 3065, 4273, 4760, and 2545.
Note. Multiprotocol extensions to BGP-4 is supported with its minimal or limited capability on OS6850
and OS9000 series switches in the current release.
To enable this implementation of BGP to support routing for multiple Network Layer protocols (e.g., IPv6,
etc.), the following capabilities are added:
• Associating a particular Network Layer protocol with the next hop information.
• Associating a particular Network Layer protocol with NLRI.
To support Multiprotocol BGP Extensions, two new non-transitive attributes are introduced, Multiproto-
col Reachable NLRI (MP_REACH_NLRI) and Multiprotocol Unreachable NLRI
(MP_UNREACH_NLRI). MP_REACH_NLRI is utilized to carry the set of reachable destinations along
with the next hop information to be used for these destinations. The MP_UNREACH_NLRI attribute
carries the set of unreachable destinations.
Multiprotocol BGP extensions support the advertisement of IPv6 prefixes over the BGP sessions estab-
lished between two BGP speakers using either of their IPv4 or IPv6 addresses. IPv6 prefixes can be redis-
tributed into BGP using route maps. Similar to IPv4 networks, IPv6 networks should also be injected into
BGP for a BGP speaker to advertise the network to its peers. A BGP speaker can support up to approxi-
mately 5000 IPv6 prefixes.
Some features that are not supported in the current release of Multiprotocol BGP include:
• Route-Reflection capability.
• AS-Confederations capability.
• IPv6 route-flap dampening.