PIM Overview Configuring PIM
page 7-12 OmniSwitch 6800/6850/9000 Advanced Routing Configuration Guide December 2007
Avoiding Register Encapsulation
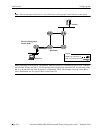
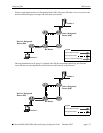
Switching to a Shortest Path Tree (SPT) topology allows PIM routers to avoid Register encapsulation of
data packets that occurs in an RPT. Register encapsulation is inefficient for the following reasons:
• The encapsulation and unencapsulation of Register messages tax router resources. Hardware routing
does not support encapsulation and unencapsulation.
• Register encapsulation may require that data travel unnecessarily over long distances. For example,
data may have to travel “out of their way” to the RP before turning back down the shared tree in order
to reach a receiver.
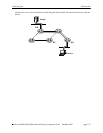
For some applications, this increased latency is undesirable. There are two methods for avoiding register
encapsulation: RP initiation of (S, G) source-specific Join messages, and switchover to a Shortest Path
Tree (SPT). For more information, refer to the sections below.
PIM-Dense Mode (PIM-DM)
PIM-DM is a multicast routing protocol that defines a multicast routing algorithm for multicast groups
densely distributed across a network. PIM-DM uses the underlying unicast routing information base to
flood multicast datagrams to all multicast routers. Prune messages are used to prevent future messages
from propagating to routers with no group membership information. It employs the same packet formats as
PIM-SM.
PIM-DM assumes that when a multicast source starts sending, all downstream systems receive multicast
datagrams. Multicast datagrams are initially flooded to all network areas. PIM-DM utilizes Reverse Path
Forwarding to prevent looping of multicast datagrams while flooding. If some areas of the network do not
have group members, PIM-DM will prune off the forwarding branch by instantiating the prune state.
PIM-DM differs from PIM-SM in two essential ways:
• There are no periodic joins transmitted, only explicitly triggered prunes and grafts.
• There is no Rendezvous Point (RP). This is particularly important in networks that cannot tolerate a
single point of failure.
Note. A PIM router cannot differentiate a PIM-DM neighbor and a PIM-SM neighbor based on Hello
messages, and PIM-DM is not intended to interact directly with a PIM-SM router.