Chapter 7 Ongoing System Management 167
The interface name bond<num> assigned by the system is dierent from the name
you give to the link aggregate port conguration. The interface name is for use at
the command line, but the port conguration name is for use in the Network pane of
System Preferences.
For example, if you enter the command ifconfig -a, the output refers to the link
aggregate using the interface name and not the port conguration name:
bond0: flags=8843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,SIMPLEX,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet6 fe80::2e0:edff:fe08:3ea6 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0xc
inet 10.0.0.12 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 10.0.0.255
ether 00:e0:ed:08:3e:a6
media: autoselect (100baseTX <full-duplex>) status: active
supported media: autoselect
bond interfaces: en1 en2 en3 en4
You do not delete or remove a link bond from the Network Pane of System
Preferences. You remove the bond through the Manage Virtual Interfaces sheet used
to create the bond.
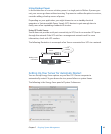
Monitoring Link Aggregation Status
You can monitor the status of a link aggregate in Mac OS X and Mac OS X Server using
the Status pane of the Network pane of System Preferences.
To monitor the status of a link aggregate:
1 Open System Preferences.
2 Click Network.
3 From the list of network interfaces on the left, choose the link aggregate port virtual
interface.
4 Click Advanced in the lower right side of the window.
5 Select the Bond Status tab.
The Status pane displays a list containing a row for each physical link in the link
aggregate. For each link, you can view the name of the network interface, its speed, its
duplex setting, the status indicators for incoming and outgoing trac, and an overall
assessment of the status.
Note: The Sending and Receiving status indicators are color-coded. Green means
the link is active (turned on) and connected. Yellow means the link is active but not
connected. Red means the link can’t send or receive trac.
6 To view more information about a link, click the corresponding entry in the list.