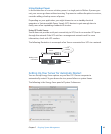
Load Balancing
One factor that can cause services to become unavailable is server overload. A server
has limited resources and can service a limited number of requests simultaneously.
If the server gets overloaded, it slows down and can eventually crash.
One way to overcome this problem is to distribute the load among a group of servers
(a server farm) using a third-party load-balancing device. Clients send requests to
the device, which then forwards the request to the rst available server based on a
predened algorithm. The clients see only a single virtual address, that of the load-
balancing device.
Many load-balancing devices also function as switches (as shown in the following
illustration), providing two functions in one, which reduces the amount of hardware
you need to use.
Server farm
Clients
Server load-
balancing switch
Note: A load-balancing device must be able to handle the aggregate (combined)
trac of the servers connected to it. Otherwise, the device becomes a bottleneck,
which reduces the availability of your servers.
Load balancing provides several advantages:
 High availability. Distributing the load among multiple servers helps you reduce the
chances that a server will fail due to server overload.
 Fault tolerance. If a server fails, trac is transparently redirected to other servers.
There might be a brief disruption of service if, for example, a server fails while a user
is downloading a le from shared storage, but the user can reconnect and restart
the le download process.
 Scalability. If demand for your services increases, you can transparently add more
servers to your farm to keep up with demand.
 Better performance. By sending requests to the least-busy servers, you can respond
faster to user requests.
168 Chapter 7 Ongoing System Management