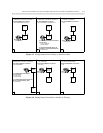
MAIN-SATELLITE/TRIBUTARY (MS/T) NETWORKS THROUGH THE UDP OR MULTIPREMISES PACKAGES 4-7
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
Routing Incoming Calls
Except for a configuration that incorporates a bypass access trunk between an ETN node and a tributary, all
calls into the MS/T complex come through the main. Calls arrive at the main from both the public and
private network.
• Public network calls arrive with the extension number.
• Private network calls are filtered through the tandem switch. If the tandem passes the call to an
intelligent main (that has either the PNA or the ETN [Standard Network] package), it sends the RNX
and the destination extension to identify the call. Otherwise, it deletes the RNX before passing the call
to the main for routing.
The main switch determines where to route the call and, for calls to other switches, sends only the
destination extension (with or without an embedded trunk DAC) to the next switch.
Routing Outgoing Calls
Public or private network calls originating at the satellite, tributary, or main reach their destination in one of
following ways:
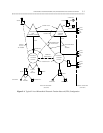
From the MS/T complex to the tandem or main:
• The caller dials the DAC of the tie trunk to the main switch (and tandem switch, if appropriate)
followed by a public network NPA-NXX-XXXX or a private network (RNX)-XXXX. This routing
capability is available on all communications systems, although its primary use is on DIMENSIONs,
System 85s, and Generic 2 communications systems that are using the Multipremises package. (See
figures 4-3(B), 4-5(G), and 4-6.)
• The caller dials an extension number that has embedded in it the DAC of the tie trunk to the next
switch. This routing capability is known as single- and multi-digit steering. It is is available on the all
communications systems, although its primary use is on DIMENSIONs, System 85s, and Generic 2
communications systems that are using the Multipremises package. (See figure 4-3(B).)
• The caller dials the destination extension and the AAR databases direct the call appropriately. This
capability is available on System 75 and Generic 1 communications systems with UDP. (See figures
4-3(C) and 4-5(I).)
• The caller dials the AAR access code (usually an 8) followed by the RNX and the extension. The AAR
databases route the call appropriately. This capability is available on intelligent mains only. (See figure
4-5(H).)
• A caller at a satellite or tributary dials the destination extension and the internal dial plan does not
contain the dialed number. Therefore, the satellite or tributary assumes the call should terminate at the
main and sends the call over the tie trunk to the main. This feature is called extended trunk access
(ETA) and is available only on the DIMENSION, System 85, and Generic 2. (See figure 4-3(A) and 4-
6(K).)