4-4 MAIN-SATELLITE/TRIBUTARY (MS/T) NETWORKS THROUGH THE UDP OR MULTIPREMISES PACKAGES
_ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
MS/T FEATURES
MS/T configurations are implemented differently on different communications systems:
• The System 75 and Generic 1 communications systems use the Uniform Dial Plan (UDP) package to
function as nodes in MS/T networks.
• DIMENSION, System 85, and Generic 2 communications systems use the Multipremises package.
• DIMENSION, System 85, and Generic 2 communications systems use the ETN (Standard Network)
package to function as intelligent mains; System 75 and Generic 1 communication systems use the
Private Network Access (PNA) package to function as intelligent mains.
Depending upon the communications system, and how it has been administered, one or more of the
following features makes it possible for a switch to perform as a node in a MS/T network (see chapter 2 for
an explanation of how MS/T software packages differ):
• Interswitch coordinated station numbering that allows each station in the MS/T complex to be assigned
a unique extension; and lets each switch in the complex have a unique block of extension numbers.
(See figure 4-2.) Coordinated station numbering underlies MS/T capabilities on all types of
communications systems.
• An internal dial plan that maps extensions to the dial access codes (DACs) of the tie trunks connecting
the switches or to RNXs. The ability to match extensions with RNXs is used on the System 75, Generic
1, and intelligent mains. The ability to match extensions with DACs is the basis of extension number
steering on the DIMENSION, System 85, and Generic 2 communications systems.
• Embedded trunk dial access codes that allow the extension number to tell the switch which tie trunk to
use for call completion. Through the internal dial plan, the first digits of the extension number may
either be equated to a trunk DAC or point to a trunk DAC. Upon recognizing the DAC, the system can
delete the prefixing digits from the extension and send the remaining digits to the destination switch. At
the destination switch, the original extension number is reconstructed. This capability is the basis of
single- and multi-digit steering on all communications systems. Single- and multi-digit steering finds its
primary use, however, on the the DIMENSION, System 85, and Generic 2 communications systems.
• AAR functionality that allows administrators to use routing patterns and trunk group preferences for call
routing. Automatic Alternate Routing (AAR) functionality is provided with the UDP, ETN (Standard
Network), and PNA packages.
• Extended Trunk Access (ETA) is a capability used only in a satellite or tributary switch. Through ETA,
calls originating on the satellite or tributary are automatically transferred to the main for processing
when they are dialed with access codes or extension numbers not administered at the satellite/tributary.
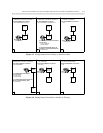
On each type of communications system, these features interact to route incoming and outgoing calls and to
transfer calls. Figures 4-3 through 4-6 show the dialing patterns associated with these features and with the
networking software that activates them.