ELECTRONIC TANDEM NETWORK (ETN) THROUGH THE ETN AND PNA PACKAGES 5-13
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
CAS
MAIN
G1/G2
AAR
RNX
334
CONSOLES
TANDEM
SYS. 75
S/T
RNX
235
INTELLIGENT
MAIN
D2000 FP8
AAR
RNX
234
CAS
BRANCH
LDN
DID
TIE LINE
TIE LINE
RLT
TANDEM
AAR
RNX
333
CAS
BRANCH
TIE
LINE
LDN
CAS
BRANCH
AAR
RNX
335
TANDEM
LDN
TIE LINE
TIE LINE
RLT
RLT
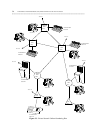
Figure 5-8. Centralized Attendant Service
Centralized Attendant Service
Centralized Attendant Service (CAS) is a feature that offers companies the ability to centralize their
attendants at a CAS main switch. Switches with their own listed directory numbers (LDNs), called CAS
branches, redirect their attendant calls over RLTs to the CAS main. The RLTs are seized only for outgoing
calls from the CAS branch and can be used only for CAS calls and CAS signaling. Either intermachine or
access tie trunks carry network calls once CAS returns the calls to their switches of origin.
CAS networks can be standalone, or, when CAS calls must be routed to a destination in another switch
after the attendant returns them to their originating switch, they can run concurrently on ETN networks. To
understand the basis of CAS design within an ETN, think of the CAS network as being superimposed upon
the ETN, since CAS software and ETN networking software coreside on the same switches. (See figure 5-
8.) In fact, when call networking is required, both CAS mains and branches are restricted to
communications systems on which AAR is running. AAR is provided through UDP or PNA on the System
75 and Generic 1 communications system; and through the ETN (Standard Network) package on the
DIMENSION, System 85, and Generic 2 communications system. Note that CAS mains can only be
DIMENSION 600 or 2000, System 75 (R1V3), System 85 (R2V2 through R2V4), and Generic 1 and Generic
2 communications systems.
Automatic Call Distribution
On Generic 1 and Generic 2 communications systems, Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) agents can
return their calls to the switch of origin for routing and processing through RLT operation. Note that RLTs
cannot be shared across features. Therefore, CAS and ACD cannot use the same RLTs.