TRANSMISSION STATES
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
_ ______________________________________________________________________________________
When you plan a communications network, there are certain rules that you cannot violate:
• Analog signals cannot be carried over digital facilities without first being converted to digital.
• Digital signals cannot be carried over analog facilities without first being converted to analog.
• Digital communication must conform to a particular protocol. Unless a protocol converter is inserted
in the transmission stream, both the originating and destination ends of the communication link must
speak the same protocol. In addition, every protocol in the transmission link must be represented twice
in the line — once as an initiator and, again, as a terminator.
To plan a network that adheres to these rules, you must be familiar with how voice or data is represented at
every stage of switching and transmission. Its mode of representation at each stage is its transmission state
at that point.
VOICE TRANSMISSION
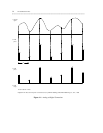
When you design a network, you must know at which points in the network the transmission state changes.
At the switch, transition points for voice signals occur before the signal enters the switch and, again, as it
exits the switch. (See figure 1-2 for the transmission states that occur with voice transmission.)
Entering the Switch
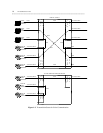
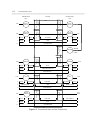
When voice is transmitted to the switch, the following processes occur depending upon the transmission
device.
• Analog telephones generate an analog signal that travels over twisted pair to an analog port on the
switch.
— If the switch is digital — like the System 75, System 85, and DEFINITY communications systems —
the port contains a codec, which converts the analog signal to a digital signal using PCM.
— On analog time-multiplexed switches, like the DIMENSION, the analog port samples the analog
signal and regenerates samples using pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM); or, on older switches, a
path through a switching matrix is found and the analog signal is applied to it directly.
• Digital voice terminals digitize the voice signal using PCM before transmitting it to a digital port on a
digital switch. No code conversion occurs at the digital port. (Note that digital voice terminals are
never attached to analog switches.)
• Incoming analog-trunk calls to a digital switch are converted to PCM by a codec built into the analog-
trunk circuit pack through which the signal enters the switch. On a time-multiplexed analog switch, the
analog-trunk signal is also converted to PAM at the trunk port.
1-7