6-16
Catalyst 3750-E and 3560-E Switch Software Configuration Guide
OL-9775-02
Chapter 6 Clustering Switches
Planning a Switch Cluster
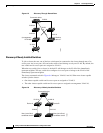
Switch Clusters and Switch Stacks
A switch cluster can have one or more Catalyst 3750-E switch stacks. Each switch stack can act as the
cluster command switch or as a single cluster member. Table 6-2 describes the basic differences between
switch stacks and switch clusters. For more information about switch stacks, see Chapter 5, “Managing
Switch Stacks.”
Recall that stack members work together to behave as a unified system (as a single switch stack) in the
network and are presented to the network as such by Layer 2 and Layer 3 protocols. Therefore, the
switch cluster recognizes switch stacks, not individual stack members, as eligible cluster members.
Individual stack members cannot join a switch cluster or participate as separate cluster members.
Because a switch cluster must have 1 cluster command switch and can have up to 15 cluster members,
a cluster can potentially have up to 16 switch stacks, totalling 144 devices.
Cluster configuration of switch stacks is through the stack master.
Table 6-2 Basic Comparison of Switch Stacks and Switch Clusters
Switch Stack Switch Cluster
Made up of Catalyst 3750-E switches only Made up of cluster-capable switches, such as
Catalyst 3750-E, Catalyst 3560-E, Catalyst 3750, and
Catalyst 2950 switches
Stack members are connected through StackWise Plus ports Cluster members are connected through LAN ports
Requires one stack master and supports up to eight other stack
members
Requires 1 cluster command switch and supports up to
15 other cluster member switches
Can be a cluster command switch or a cluster member switch Cannot be a stack master or stack member
Stack master is the single point of complete management for
all stack members in a particular switch stack
Cluster command switch is the single point of some manage-
ment for all cluster members in a particular switch cluster
Back-up stack master is automatically determined in case the
stack master fails
Standby cluster command switch must be pre-assigned in case
the cluster command switch fails
Switch stack supports up to eight simultaneous stack master
failures
Switch cluster supports only one cluster command switch
failure at a time
Stack members (as a switch stack) behave and is presented as
a single, unified system in the network
Cluster members are various, independent switches that are
not managed as and do not behave as a unified system
Integrated management of stack members through a single
configuration file
Cluster members have separate, individual configuration files
Stack- and interface-level configurations are stored on each
stack member
Cluster configuration are stored on the cluster command
switch and the standby cluster command switch
New stack members are automatically added to the switch
stack
New cluster members must be manually added to the switch
cluster