3-28
Cisco ASA Series Firewall ASDM Configuration Guide
Chapter 3 Information About NAT (ASA 8.3 and Later)
NAT for VPN
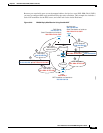
Figure 3-23 Interface PAT and Identity NAT for Site-to-Site VPN
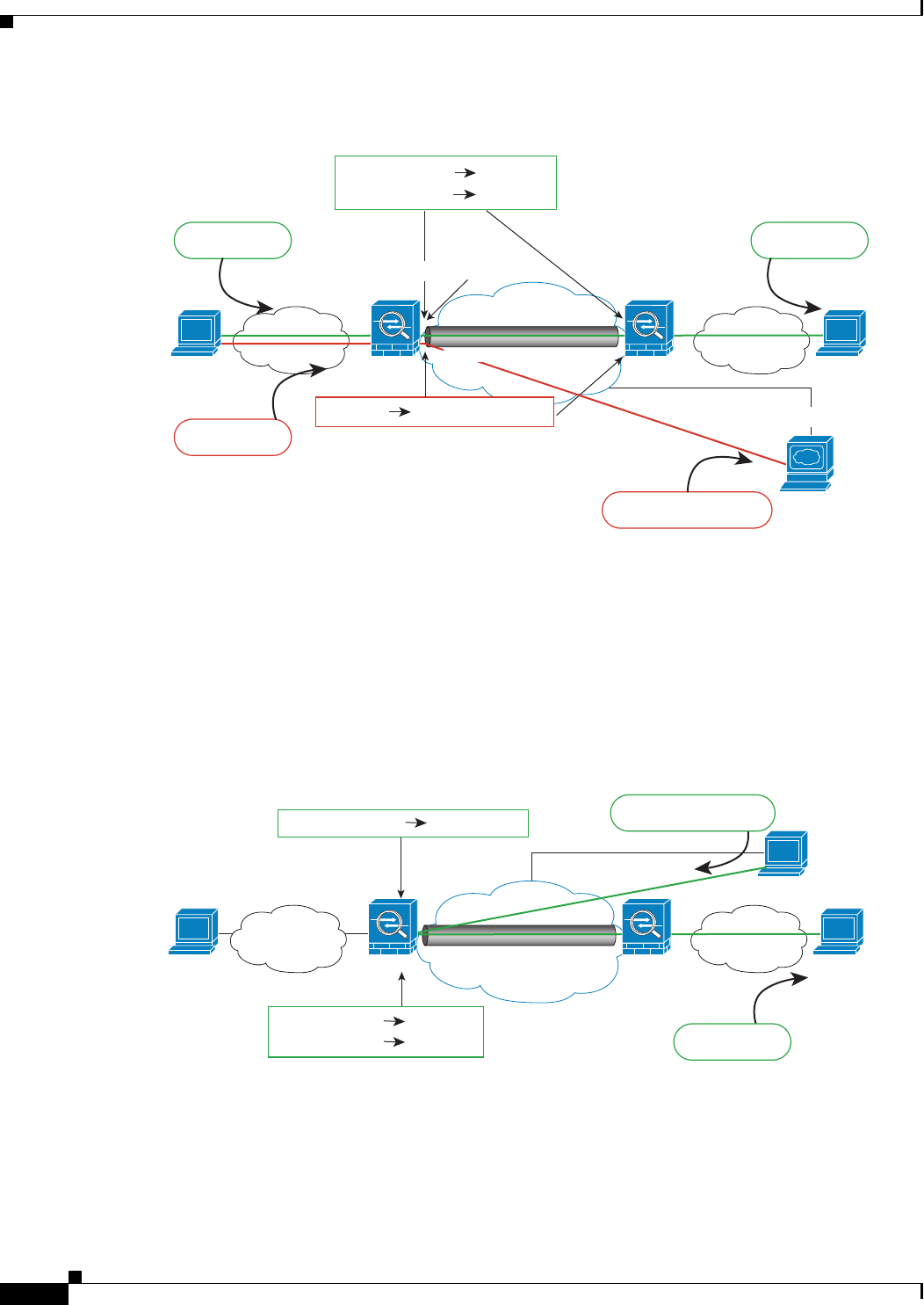
Figure 3-24 shows a VPN client connected to ASA1 (Boulder), with a Telnet request for a server
(10.2.2.78) accessible over a site-to-site tunnel between ASA1 and ASA2 (San Jose). Because this is a
hairpin connection, you need to enable intra-interface communication, which is also required for
non-split-tunneled Internet-bound traffic from the VPN client. You also need to configure identity NAT
between the VPN client and the Boulder & San Jose networks, just as you would between any networks
connected by VPN to exempt this traffic from outbound NAT rules.
Figure 3-24 VPN Client Access to Site-to-Site VPN
See the following sample NAT configuration for ASA1 (Boulder):
! Enable hairpin for VPN client traffic:
same-security-traffic permit intra-interface
! Identify local VPN network, & perform object interface PAT when going to Internet:
10.1.1.6
ASA1 ASA2
10.2.2.78
Internet
Src: 10.1.1.6
10.1.1.6
203.0.113.1:6070
Src: 10.1.1.6 10.1.1.6
Dst: 10.2.2.78 10.2.2.78
San Jose
Inside
Boulder
Inside
1. IM to 10.2.2.78
Src: 10.1.1.6
A. HTTP to
www.example.com
Src: 10.1.1.6
3. IM received
C. HTTP request to www.example.com
2. Identity NAT between NWs connected by VPN
B. ASA performs interface PAT for
outgoing traffic.
Src: 203.0.113.1:6070
www.example.com
ASA Outside IP: 203.0.113.1
303459
Site-to-Site VPN Tunnel
VPN Client
209.165.201.10
10.1.1.6
ASA1 ASA2
10.2.2.78
Internet
San Jose
Inside
Boulder
Inside
Site-to-Site VPN Tunnel
4. HTTP request received
1. HTTP request to 10.2.2.78
10.3.3.10209.165.201.10
2. ASA decrypts packet; src address is
now local address
Src: 10.3.3.10 10.3.3.10
Dst: 10.2.2.78 10.2.2.78
3. Identity NAT between VPN Client &
San Jose NWs; intra-interface config req’d
Src: 209.165.201.10
Src: 10.3.3.10
303460