5/26/05 Acknowledging Rogue Access Points
OL-7426-03
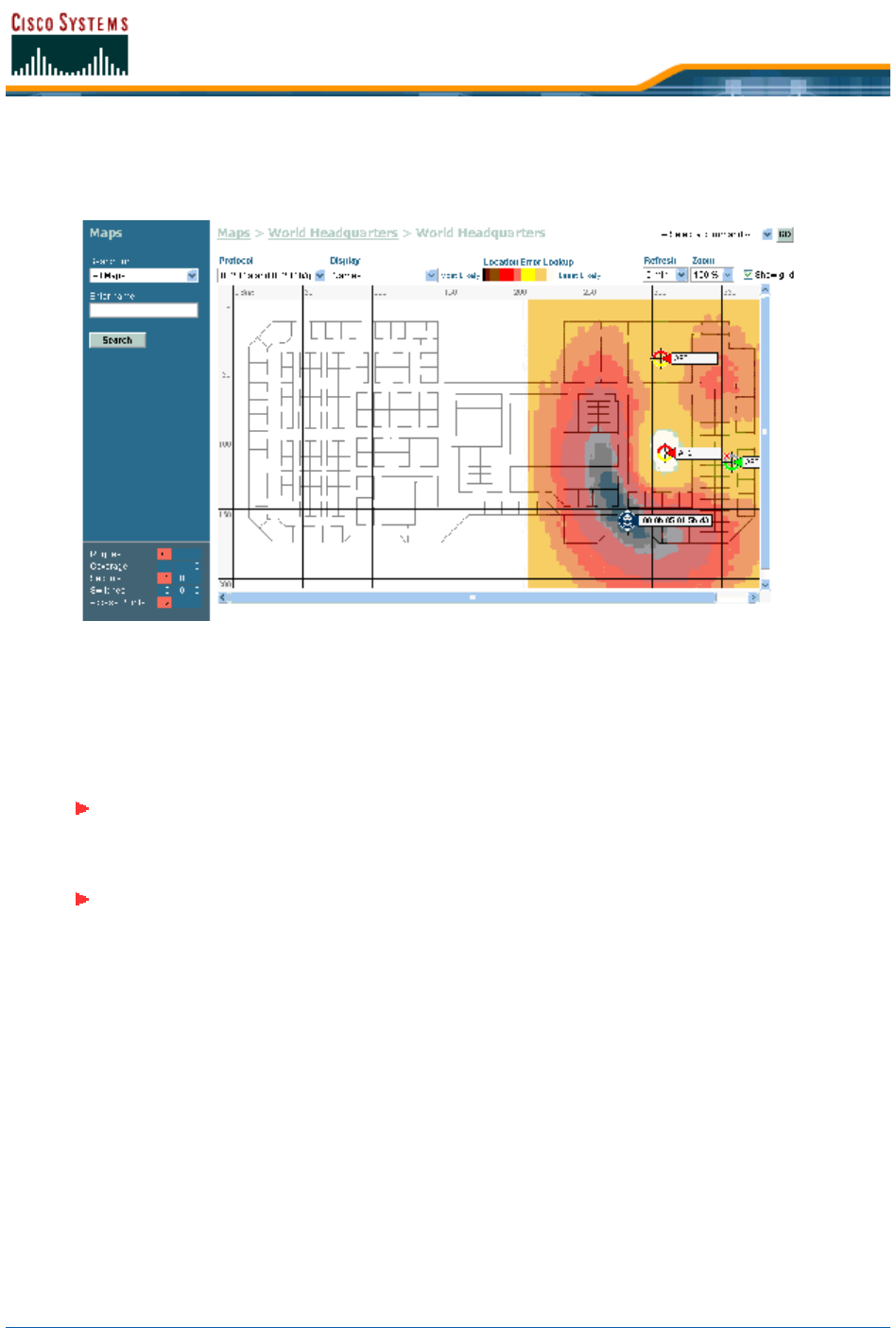
• In the Alarms > Rogue AP <MAC address> page, select Map to have Cisco WCS display the
current calculated rogue access point location on the Maps > <building name> > <floor
name> page.
Note that Cisco WCS Location compares RSSI signal strength from two or more Cisco 1000
Series lightweight access points to find the most probable location of the rogue access point,
and places a small “skull-and-crossbones” indicator at its most likely location.
Note that Cisco WCS Base function compares RSSI signal strength from the rogue access point,
and places a small “skull-and-crossbones” indicator next to the Cisco 1000 Series lightweight
access point receiving the strongest RSSI signal from the rogue access point.
Acknowledging Rogue Access PointsAcknowledging Rogue Access Points
• To acknowledge known rogue access points, navigate to the Rogue AP Alarms page.
Right-click the rogue access point (red, unknown) to be acknowledged, and select Set State to
‘Known Internal’ or Set State to ‘Known External’. In either case, the red rogue access
point entry is removed from the Alarms Page.
Locating ClientsLocating Clients
The Cisco WCS allows system operators to locate clients in the enterprise. Do the following:
• Use Monitor/Clients to navigate to the Clients Summary page.
• On the Clients Summary page, in the left sidebar Search for All Clients to have Cisco WCS
display the Clients page.
Note: When the rogue access point does not receive a packet from the rogue access
point client, Cisco WCS cannot reliably determine the rogue access point client
location.
Note: When the rogue access point does not receive a packet from the rogue access
point client, Cisco WCS cannot reliably determine the rogue access point client
location.