D-Link DES-3010FA/GA User Guide
Page 148
Defining Multiple Spanning Tree
Multiple Spanning Tree (MSTP) provides differing load balancing scenarios. For example, while port A is blocked
in one STP instance, the same port can be placed in the Forwarding state in another STP instance. The MSTP
Properties Page contains information for defining global MSTP settings, including region names, MSTP revisions,
and maximum hops. To define MSTP:
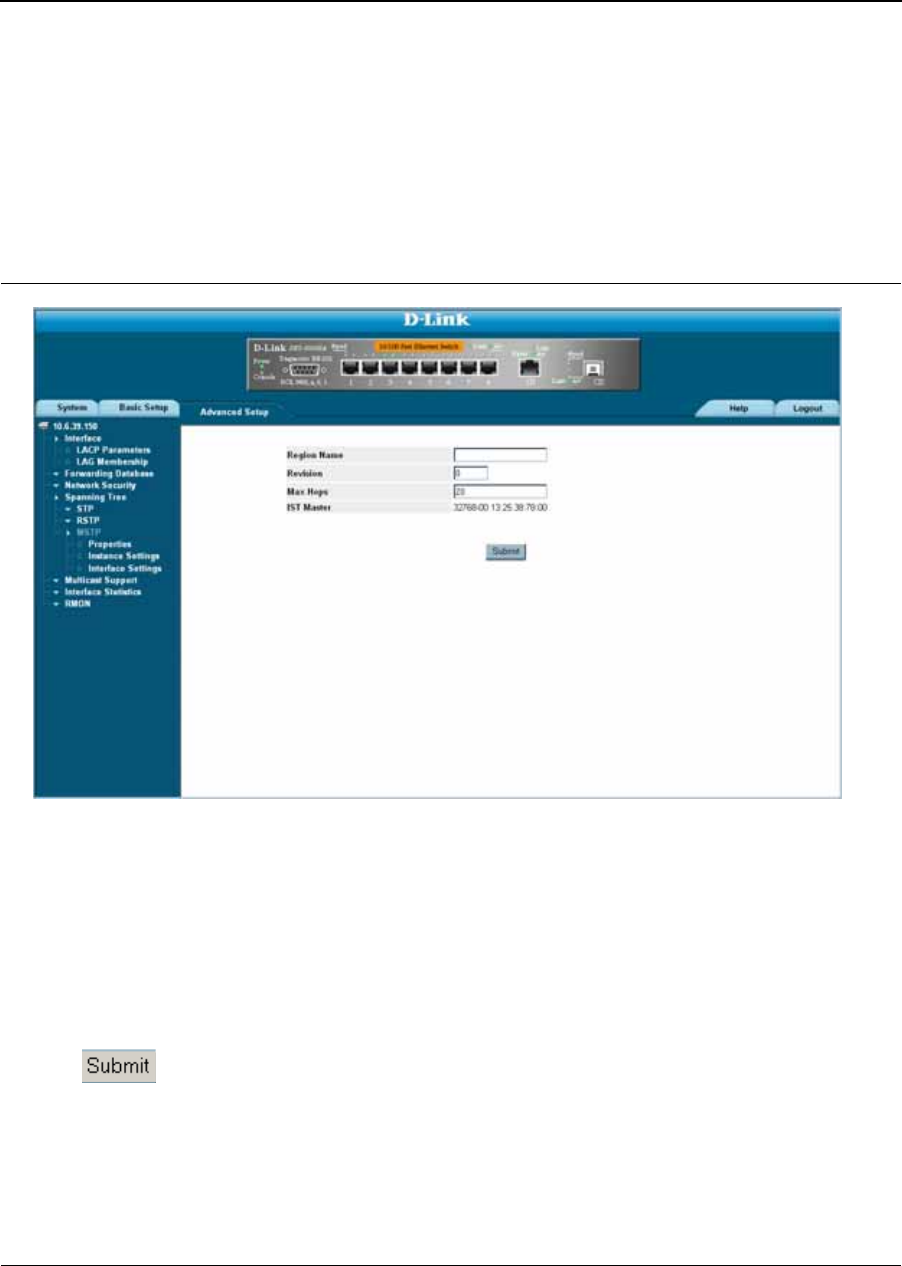
1. Click Advanced Setup > Spanning Tree > MSTP > Properties. The MSTP Properties Page opens:
Figure 90: MSTP Properties Page
The MSTP Properties Page contains the following fields:
• Region Name — User-defined STP region name.
• Revision — An unsigned 16-bit number that identifies the revision of the current MSTP configuration. The
revision number is required as part of the MSTP configuration. The possible field range is 0-65535.
•
Max Hops
— Specifies the total number of hops that occur in a specific region before the BPDU is discarded.
Once the BPDU is discarded, the port information is aged out. The possible field range is 1-40. The field default
is 20 hops.
• IST Master
—
Identifies the Spanning Tree Master instance. The IST Master is the specified instance root.
2. Define the Region Name, Revision, and Max Hops fields.
3. Click . The MSTP properties are defined, and the device is updated.
Defining MSTP Instance Settings
MSTP maps VLANs into STP instances. Packets assigned to various VLANs are transmitted along different paths
within Multiple Spanning Tree Regions (MST Regions). Regions are one or more Multiple Spanning Tree bridges


















