A.3 Bus Phases
Appendix A-13
A.3.3 SELECTION phase
The SELECTION phase allows an initiator to select a target for the purpose of initiating some target
function (e.g., READ or WRITE command). During the SELECTION phase the I/O signal is
negated so that this phase can be distinguished from the RESELECTION phase.
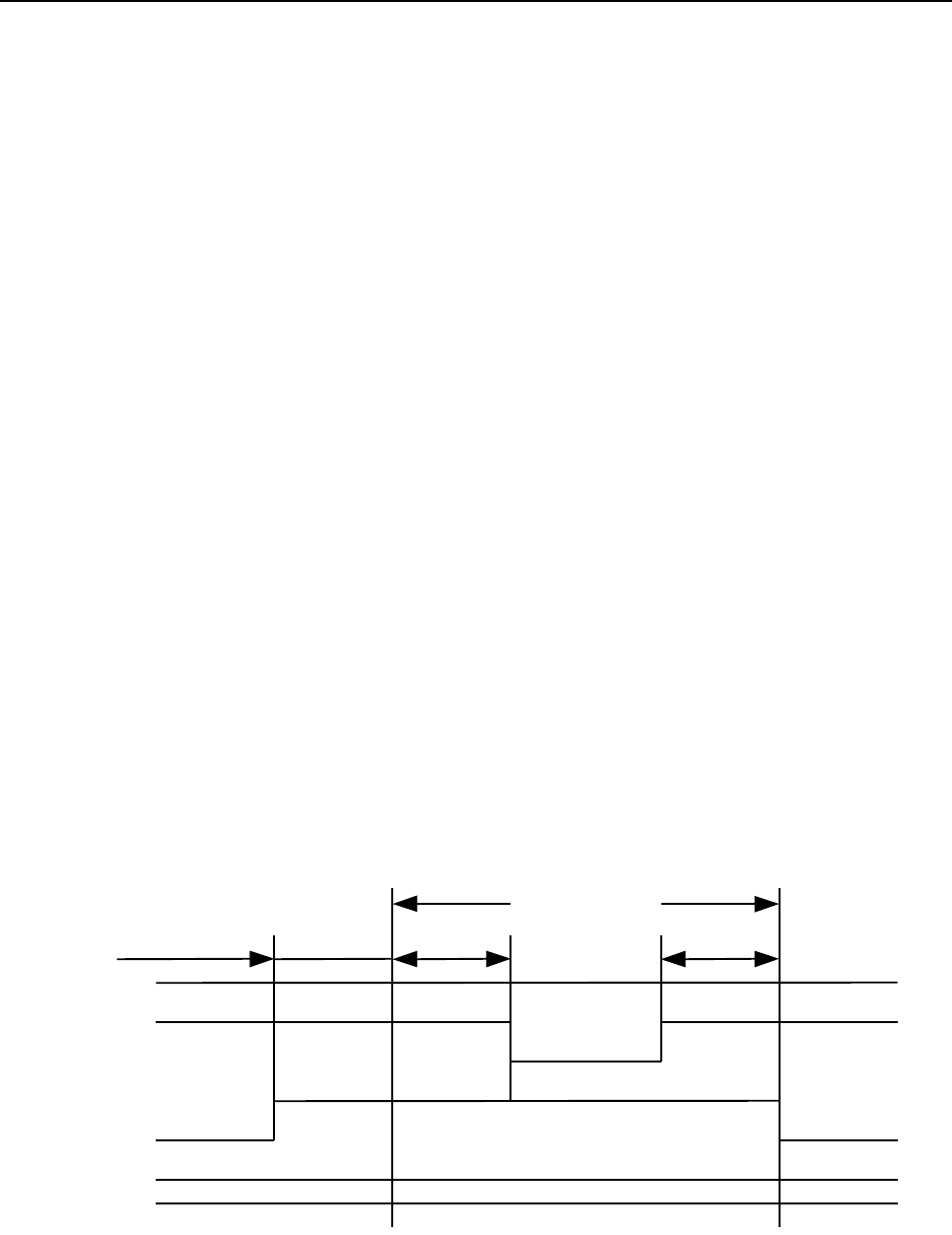
1) The SCSI device that won the arbitration has both the BSY and SEL signals asserted and has
delayed at least a bus clear delay plus a bus settle delay before ending the ARBITRATION
phase. The SCSI device that won the arbitration becomes an initiator by not asserting the I/O
signal.
2) The initiator shall set the DATA BUS to a value which is the OR of its SCSI ID bit and the
target fs SCSI ID bit, and it shall assert the ATN signal.
3) The initiator shall then wait at least two deskew delays and release the BSY signal.
4) The initiator shall then wait at least a bus settle delay before looking for a response from the
target.
5) The target shall determine that it is selected when the SEL signal and its SCSI ID bit are true
and the BSY and I/O signals are false for at least a bus settle delay. The selected target may
examine the DATA BUS in order to determine the SCSI ID of the selecting initiator. The
selected target shall then assert the BSY signal within a selection abort time of its most recent
detection of being selected; this assertion is required for correct operation of the selection
time-out procedure.
The target shall not respond to a selection if bad parity is detected. Also, if more than two
SCSI ID bits are on the DATA BUS, the target shall not respond to selection.
6) No less than two deskew delays after the initiator detects the BSY signal is true, it shall
release the SEL signal and may change the DATA BUS. The target shall wait until the SEL
signal is false before asserting the REQ signal to enter an information transfer phase.
deskew
delay
x
2
bus clear delay
+ bus settle
delay
deskew
delay
x
2
SELECTION phase
I/O
BSY
SEL
DB


















