Chapter 1. Technical description 21
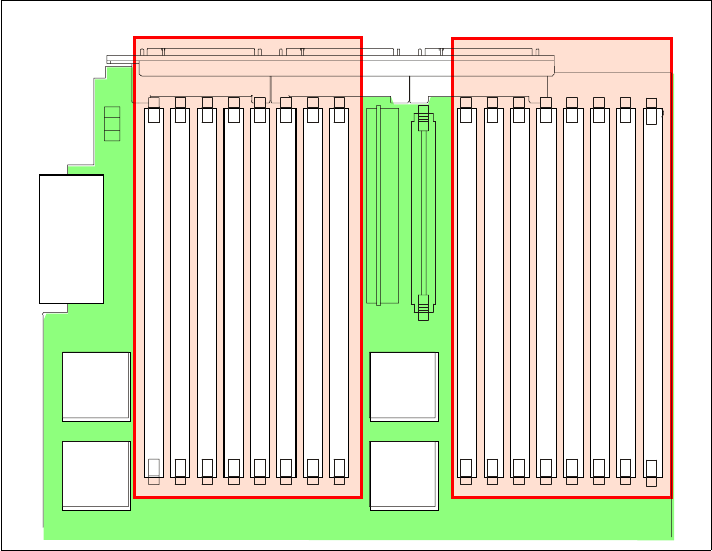
Memory mirroring
Memory mirroring is roughly equivalent to RAID-1 in disk arrays, in that
memory is divided in two ports and one port is mirrored to the other half (see
Figure 1-12). If 8 GB is installed, then the operating system sees 4 GB once
memory mirroring is enabled (it is disabled in BIOS by default). All mirroring
activities are handled by the hardware without any additional support required
from the operating system.
Figure 1-12 Memory DIMMs are divided into two ports
When memory mirroring is enabled (see 4.1.2, “Enabling memory mirroring”
on page 108), the data that is written to memory is stored in two locations.
One copy is kept in the port 1 DIMMs, while a second copy is kept in the
port 2 DIMMs. During the execution of the read command, the data is read
from the DIMM with the least amount of reported memory errors through
memory scrubbing.
If memory scrubbing determines the DIMM is damaged beyond use, read and
write operations are redirected to the partner DIMM in the other port. Memory
scrubbing then reports the damaged DIMM and the Light Path Diagnostics
display the error. If memory mirroring is enabled, then the mirrored copy of the
Port 1 Port 2


















