Disk Environment Overview 95
DB2 fully integrates concurrent copy into DB2 recovery. The CONCURRENT
option on the DB2 COPY utility reduces disruption and automatically manages
the copies used for recovery, to ensure consistent data. This option invokes the
concurrent copy function of DFSMSdss, and records the resulting image copies in
the SYSCOPY table of the DB2 catalog. “Image Copy Options” on page 20 has
more information about DB2 use of concurrent copy.
Concurrent copy is called through the
DFSMSdss standard API. DB2 COPY with
the CONCURRENT keyword calls this API
for full image copies. DB2 RECOVER
recognizes that type of image copy. Other callers of concurrent copy are IMS,
CICS (backup while open), and DFSMShsm.
9.5.3 Virtual Concurrent Copy
Virtual concurrent copy extends the benefits of concurrent copy to users who
have RVA installed with SnapShot. When the CONCURRENT keyword is
specified on a DFSMSdss COPY or DUMP statement, the software can detect
whether you have a 3990 storage control or an RVA. If you have an RVA, the
virtual concurrent copy function is invoked. If all the criteria are met for
DFSMSdss SnapShot, a DFSMSdss SnapShot will be performed in preference to
a concurrent copy.
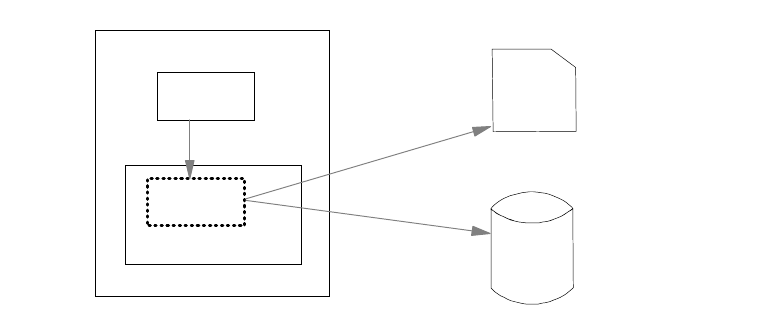
The logical completion of the point-in time copy occurs when the source data is
snapped into an interim data set called the working space data set (WSDS). The
physical completion occurs when the data is moved by DFSMSdss to the target
tape or disk data set. Once copy is logically complete, the data can be made
available for application updates. Figure 27 on page 95 explains the four steps of
a virtual concurrent copy operation.
Figure 27. Virtual Concurrent Copy Operation Steps
When concurrent copy is already in use, it is not necessary to change the JCL to
use virtual concurrent copy. As concurrent copy support is incorporated into the
backup and recovery utilities of DB2, IMS, and CICS, virtual concurrent copy can
take advantage of this support immediately and without any change.
9.5.4 Remote Copy
Remote copy continuously duplicates on a remote (secondary) storage server
any update done on a local (primary) storage server
. The objective is to provide
an application independent disaster recovery solution. The problem with
4) Physical copy
complete
WSDS
1) SNAP
3) DFSMSdss data mover
2) Logical copy complete
Source
Target
Ta r ge t


















