98 Storage Management with DB2 for OS/390
This replaces a manual site switch process that could require more than 20
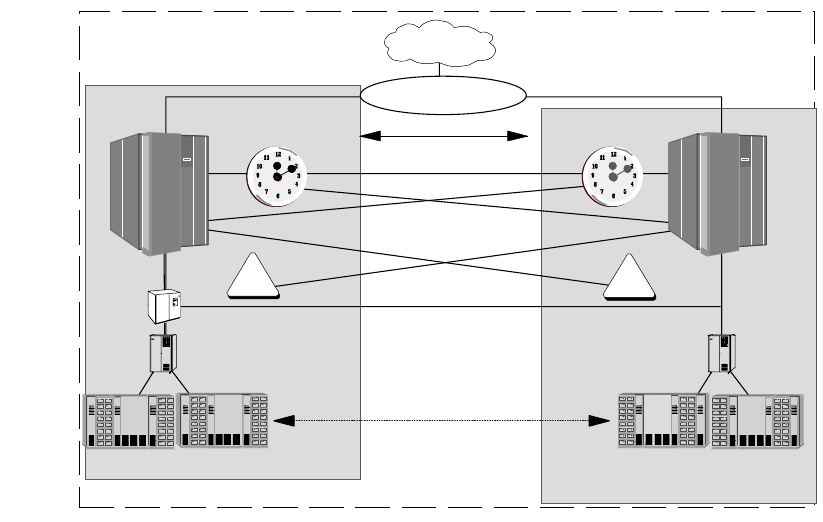
people to be present to perform their specialized tasks. Figure 30 on page 98
shows the global GDPS architecture.
Figure 30. GDPS Architecture
Implementation
GDPS is being implemented as an automation solution, using standard sysplex
and IBM 3990 Storage Control Unit functions. The base for the implementation of
a GDPS is a sysplex spread across two sites, securing diagnostic and control
capability in case of a site failure. The two sites may be up to 40 km apart.
The sysplex must be configured to be fault tolerant: this applies to the sysplex
control data sets and to the Sysplex Timer and Coupling Facilities (if used). A
fault-tolerant Sysplex Timer configuration consists of two interconnected timers,
properly connected to all processor complexes that are part of the sysplex.
All data required for an application restart must be DASD resident. All data that is
part of the same group of applications must be in one site, and PPRC must be
used to maintain a
synchronous copy of the data in the backup location. Spare
processor capacity and/or expendable workload must be available in the
secondary site so that enough capacity is available to resume the critical
workload in the backup location.
Processing
GDPS processing is initialized based on a GDPS configuration database that
contains site and configuration details. This allows GDPS to support and
automate the routine PPRC configuration management tasks such as setting up
links and pairs, to perform an interval driven check on the
current status of the
configuration and compare it against the
target configuration status.
Remote Copy
Network
Site
B
Site
A
Local
DASD
Primary
DASD
40km Max Distance
CF
9037-2 9037-2
High Performance
Routing
Secondary
DASD
Local
DASD
CF