42 Storage Management with DB2 for OS/390
DFSMShsm's automatic backup services, supported by concurrent copy, to help
with point of consistency backups.
It is not advisable to use HSM to manage most production databases. Therefore,
use a NOMIGRATE Management Class for this type of data. This prevents HSM
space and availability management from operating. Specifically, AUTO BACKUP
is set to NO so that HSM does not back up the data set, ADMIN OR USER
COMMAND BACKUP is set to NONE to prevent manual backup, and expiration
attributes are set to NOLIMIT to prevent data set deletion.
Although production database data does receive automatic backup service,
DFSMSdss can be set to run concurrent copy for production databases.
ACCESSIBILITYmay be set to CONTINUOUS for Storage Classes assigned to
production databases to ensure that the data set is allocated behind a storage
control with concurrent copy support.
Testing or end user databases that have less critical availability requirements can
benefit from system management using HSM. Additionally, selected data types
for production systems could also be effectively managed using HSM.
For DB2 systems, it is possible to manage archive logs and image copies with
HSM. These data sets can be retained on primary devices for a short period of
time, and then migrated directly to tape (ML2).
HSM uses the same ML2 tape until it is full. Therefore, unless another
mechanism is used, to avoid placing consecutive archive logs on the same ML2
tape, ensure that the storage administrator defines the HSM parameter
SETSYS(PARTIALTAPE(MARKFULL), so it uses a new ML2 tape each time
space management is executed.
Requirements should be agreed upon by the storage administrator and the DBA.
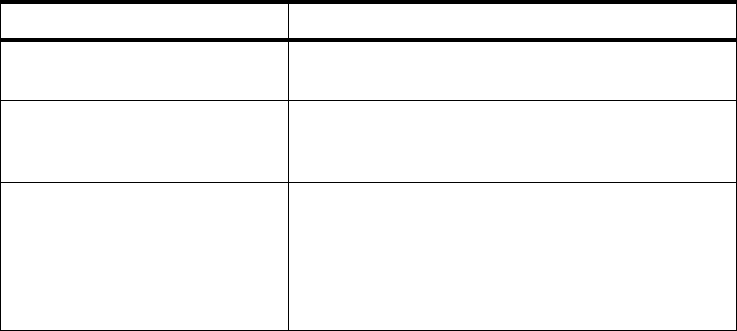
Table 10 on page 42 displays a list of attributes for consideration.
Table 10. Management Class Attributes
ATTRIBUTE COMMENT
Space management - Release unused space in the data set (applies to
non-VSAM only).
Expiration - Delete data set after a number of days or a date.
- Delete after a number of days of non usage.
- Use of Retention or Expiration periods.
Migration - What method a data set can migrate (Command
or automatically, or both).
- Number of days non-usage on level 0 volumes
before migration commences.
- Number of days non-usage on level 1 volumes
before migration commences.


















