104 Storage Management with DB2 for OS/390
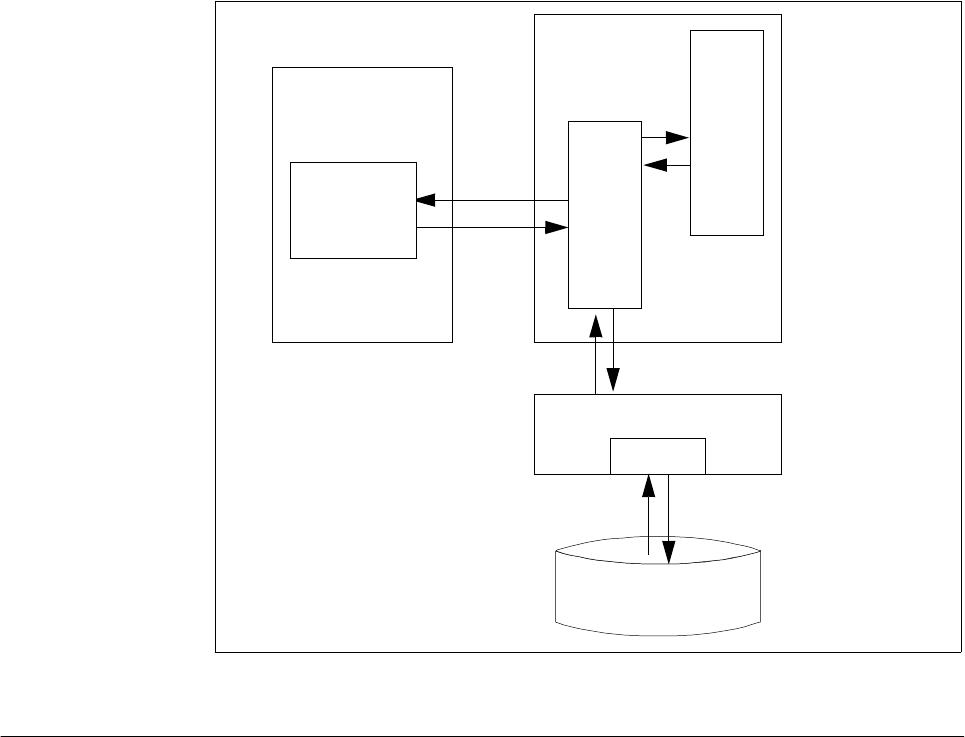
Figure 32. Storage Hierarchy
10.2 Data Read Operations
DB2 uses four read mechanisms to get data pages from disk into the virtual
bufferpool:
• Normal read (or synchronous read)
• Sequential prefetch
• Dynamic prefetch
• List sequential prefetch
10.2.1 Normal Read
Normal read is used when just one or a few consecutive pages are retrieved. The
unit of transfer for a normal read is one page. This read is referred to in DB2 PM
reports as synchronous read. See
A in Figure 33 on page 109.
10.2.2 Sequential Prefetch
When the optimizer chooses sequential prefetch as access path, sequential
prefetch is performed concurrently with other operations of the originating
application program. It brings pages into the virtual buffer pool before they are
required and reads several pages with a single I/O operation. Because this read
executes concurrently and independently of the application program, it is referred
to in DB2 PM reports as asynchronous read. See
B in Figure 33 on page 109. Of
course, not all asynchronous I/O can be performed concurrently; there can be
CONTROLLER
CACHE
Coupling
Facility
Group
Buffer
Pool
DB2
Vitual
Buffer Pool
DB2
Hiper Pool
CPC