Understanding IP Addressing E-3
Subnet masks
To create subnets, the network manager must define a subnet mask, a 32-bit number that indicates which bits
in an IP address are used for network and subnetwork addresses, and which are used for host addresses. One
subnet mask should apply to all IP networks that are physically connected together and share a single assigned
network number. Subnet masks are often written in decimal notation, like IP addresses, but they are most
easily understood in binary notation. When a subnet mask is written in binary notation, each numeral 1
indicates that the corresponding bit in the IP address is part of the network or subnet address. Each 0
indicates that the corresponding bit is part of the host address. The following table shows the proper subnet
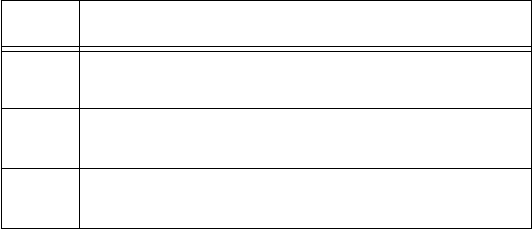
masks to use for each class of network, when no subnets are required.
To know whether subnets are being used or not, you must know what subnet mask is being used—you cannot
determine this information simply from an IP address. Subnet mask information is configured as part of the
process of setting up IP routers and gateways such as the Netopia R3100.
Note: If you receive a routed account from an ISP, there must be a mask associated with your network IP
address. By using the IP address with the mask you can discover exactly how many IP host addresses you
actually have.
To configure subnets properly, you must also be able to convert between binary notation and decimal notation.
Example: Using subnets on a Class C IP internet
When setting up IP routing with a Class A Address, or even multiple Class C Addresses, subnetting is fairly
straightforward. Subnetting a single Class C address between two networks, however, is more complex. This
section describes the general procedures for subnetting a single Class C network between two Netopia routers
so that each can have Internet access.
Class Subnet mask for a network with no subnets
A
Binary: 11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000
Decimal: 255.0.0.0
B
Binary: 11111111.11111111.00000000.00000000
Decimal: 255.255.0.0
C
Binary: 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000
Decimal: 255.255.255.0


















