4 – Managing Switches
Configuring a Switch
4-26 59226-00 B
S
4.7.4.1
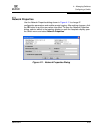
IP Configuration
The IP configuration identifies the switch on the Ethernet network and determines
which network discovery method to use. Table 4-6 describes the IP configuration
parameters.
Table 4-6. IP Configuration Parameters
Parameter Description
Network Discov-
ery
Choose one of the following methods by which to assign the IP
address:
Static - Uses the IP configuration parameters entered in the
Switch Properties dialog.
BootP - Acquires the IP configuration from a BootP server.
RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) - Acquires the IP
address from an RARP server. An RARP request is broadcast
with up to three retries, each at 5 second intervals. If no IP
address is obtained, the switch reverts to the previously config-
ured IP address.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) - Acquires the IP
configuration from a DHCP server. If no satisfactory lease is
obtained, the DHCP client attempts to use the previously config-
ured lease. If the previous lease cannot be used, no IP address
will be assigned to this switch in order to avoid an IP address
conflict. The DHCP server must then be made available.
If a BootP, RARP, or DHCP server is not available, the switch will
attempt to use a previously assigned valid lease. If no lease was
ever assigned, the switch will attempt to use the previously assigned
static IP address.
IP Address Internet Protocol (IP) address for the Ethernet port. The default value
is 10.0.0.1.
Subnet mask Subnet mask address for the Ethernet port. The default value is
255.0.0.0.
Gateway IP gateway address. The default value is 10.0.0.254.