Chapter 7 Storage
NSA320 User’s Guide
171
shows disks in a single JBOD volume. Data is not written across disks but written
sequentially to each disk until it’s full.
RAID 0
RAID 0 spreads data evenly across two or more disks (data striping) with no
mirroring nor parity for data redundancy, so if one disk fails the entire volume will
be lost. The major benefit of RAID 0 is performance. The following figure shows
two disks in a single RAID 0 volume. Data can be written and read across disks
simultaneously for faster performance.
RAID 0 capacity is the size of the smallest disk multiplied by the number of disks
you have configured at RAID 0 on the NSA. For example, if you have two disks of
sizes 100 GB and 200 GB respectively in a RAID 0 volume, then the maximum
capacity is 200 GB (2 * 100 GB, the smallest disk size) and the remaining space
(100 GB) is unused.
Typical applications for RAID 0 are non-critical data (or data that changes
infrequently and is backed up regularly) requiring high write speed such as audio,
video, graphics, games and so on.
RAID 1
RAID 1 creates an exact copy (or mirror) of a set of data on another disk. This is
useful when data backup is more important than data capacity. The following
Table 26 JBOD
A1 B1
A2 B2
A3 B3
A4 B4
DISK 1 DISK 2
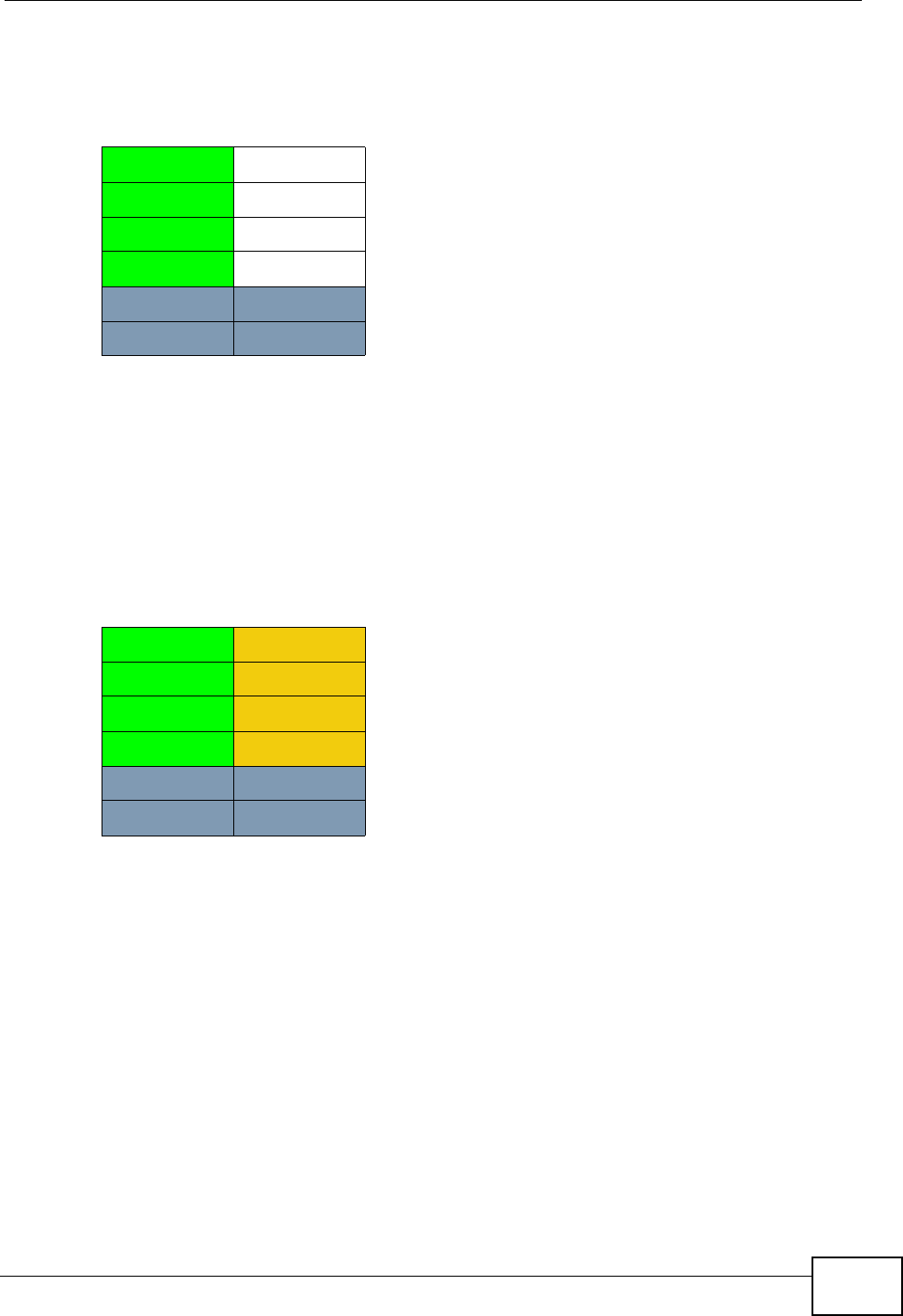
Table 27 RAID 0
A1 A2
A3 A4
A5 A6
A7 A8
DISK 1 DISK 2


















