Configuring Switching Information 451
To prevent DHCP packets from being used as a DoS attack when DHCP snooping is enabled, the
snooping application enforces a rate limit for DHCP packets received on untrusted interfaces. DHCP
snooping monitors the receive rate on each interface separately. If the receive rate exceeds the
configuration limit, DHCP snooping brings down the interface. The port must be administratively
enabled from the Switching
→
Ports
→
Port Configuration page (or the no shutdown CLI command)
to further work with the port. You can configure both the rate and the burst interval.
The DHCP snooping application processes incoming DHCP messages. For DHCPRELEASE and
DHCPDECLINE messages, the application compares the receive interface and VLAN with the client’s
interface and VLAN in the binding database. If the interfaces do not match, the application logs the
event and drops the message. For valid client messages, DHCP snooping compares the source MAC
address to the DHCP client hardware address. Where there is a mismatch, DHCP snooping logs and
drops the packet. You can disable this feature using the DHCP Snooping Interface Configuration page
or by using the no ip dhcp snooping verify mac-address command. DHCP snooping
forwards valid client messages on trusted members within the VLAN. If DHCP relay and/or DHCP server
co-exist with the DHCP snooping, the DHCP client message will be sent to the DHCP relay and/or
DHCP server to process further.
To access the DHCP Snooping Interface Configuration page, click Switching
→
DHCP Snooping
→
Interface Configuration in the navigation tree.
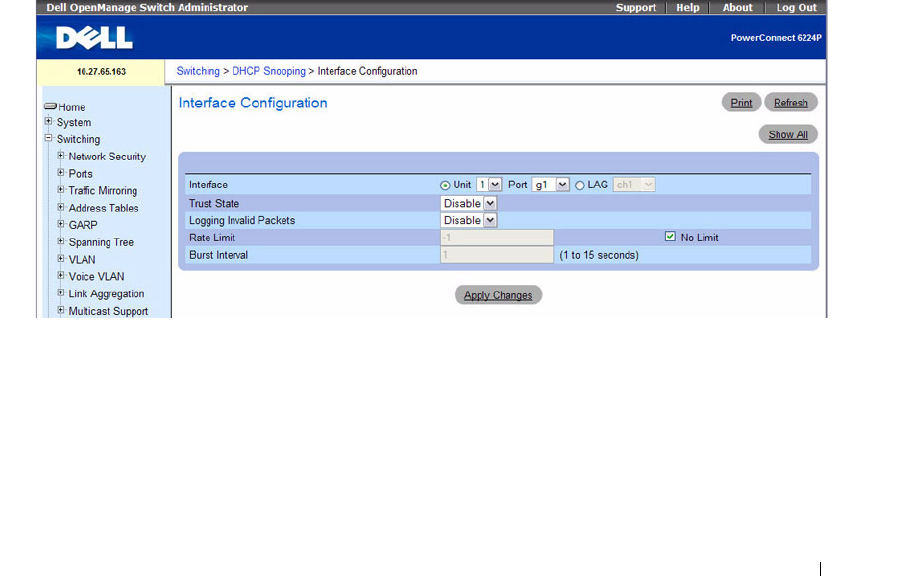
Figure 7-115. DHCP Snooping Interface Configuration
The DHCP Snooping Interface Configuration page contains the following fields:
•
Port
— Select the interface for which data is to be displayed or configured.
•
Trust State
— If it is enabled, the DHCP snooping application considers the port as trusted. The
default is Disable.


















