C141-E090-01EN4 - 12
4.6.4 Synthesizer circuit
The drive uses constant density recording to increase total capacity. This is different from the
conventional method of recording data with a fixed data transfer rate at all data area. In the
constant density recording method, data area is divided into zones by radius and the data
transfer rate is set so that the recording density of the inner cylinder of each zone is nearly
constant. The drive divides data area into 15 zones to set the data transfer rate. Table 4.2
describes the data transfer rate and recording density (BPI) of each zone.
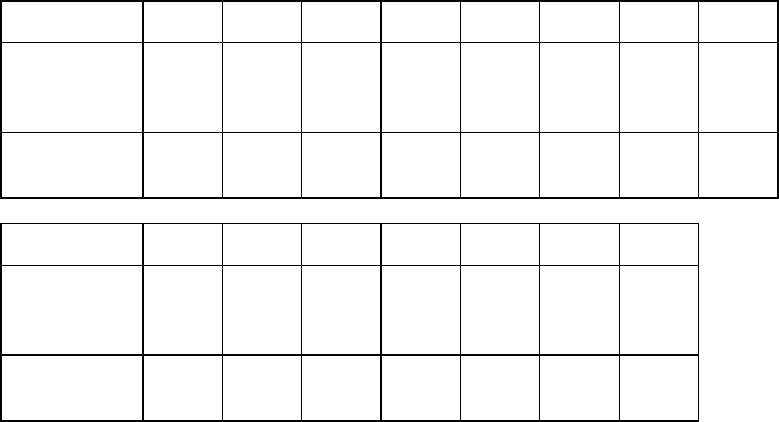
Table 4.2 Write clock frequency and transfer rate of each zone
Zone 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Cylinder 0
to
1230
1231
to
2560
2561
to
3820
3821
to
5610
5611
to
6510
6511
to
6940
6941
to
8640
8641
to
9530
Transfer rate
[MB/s]
40.69 40.69 39.67 38.08 37.21 36.78 34.90 33.89
Zone 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Cylinder 9531
to
10870
10871
to
11530
11531
to
12200
12201
to
13300
13301
to
14030
14031
to
15160
15161
to
15870
Transfer rate
[MB/s]
32.29 31.42 30.58 29.10 28.09 26.49 24.54
The MPU transfers the data transfer rate setup data to the RDC that includes synthesizer circuit
to change the data transfer rate.
4.7 Servo Control
The actuator motor and the spindle motor are submitted to servo control. The actuator motor
is controlled for moving and positioning the head to the track containing the desired data. To
turn the disk at a constant velocity, the actuator motor is controlled according to the servo data
that is written on the data side beforehand.
