14 • Chapter 4 Communication DMC-2X00
Switch
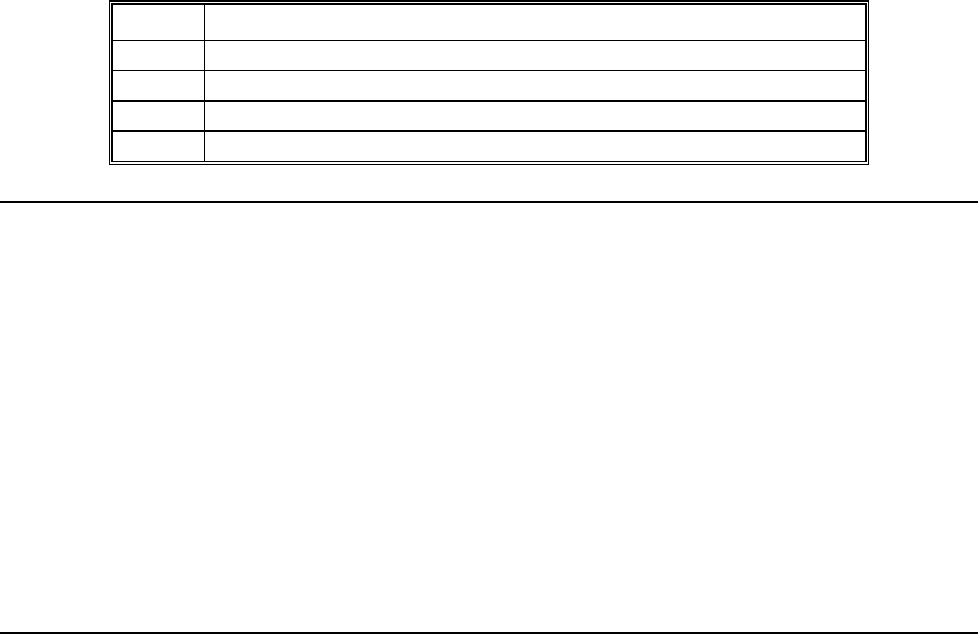
Coordinated Motion Status Information for S or T plane (2 Byte)
BIT 15 BIT
14
BIT 13 BIT 12 BIT 11 BIT
10
BIT 9 BIT 8
Move in
Progress
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
BIT 7 BIT 6 BIT 5 BIT 4 BIT 3 BIT 2 BIT 1 BIT 0
N/A N/A Motion is
slewing
Motion is
stopping due
to ST or
Limit
Switch
Motion is
making
final
decel.
N/A N/A N/A
Notes Regarding Velocity and Torque Information
The velocity information that is returned in the data record is 64 times larger than the value returned
when using the command TV (Tell Velocity). See command reference for more information about
TV.
The Torque information is represented as a number in the range of +/-32767. Maximum negative
torque is -32767. Maximum positive torque is 32767. Zero torque is 0.
QZ Command
The QZ command can be very useful when using the QR command, since it provides information
about the controller and the data record. The QZ command returns the following 4 bytes of
information.
BYTE # INFORMATION
0 Number of axes present
1 number of bytes in general block of data record
2 number of bytes in coordinate plane block of data record
3 Number of Bytes in each axis block of data record
Controller Response to Commands
Most DMC-2x00 instructions are represented by two characters followed by the appropriate
parameters. Each instruction must be terminated by a carriage return or semicolon.
Instructions are sent in ASCII, and the DMC-2x00 decodes each ASCII character (one byte) one at a
time. It takes approximately 0.5 msec for the controller to decode each command. However, the PC
can send data to the controller at a much faster rate because of the FIFO buffer.
After the instruction is decoded, the DMC-2x00 returns a response to the port from which the
command was generated. If the instruction was valid, the controller returns a colon (:) or a question
mark (?) if the instruction was not valid. For example, the controller will respond to commands which
are sent via the USB port back through the USB port, to commands which are sent via the main RS-
232 port back through the RS-232 port, and to commands which are sent via the Ethernet port back
through the Ethernet port.