BIOS Intel® Server Board SDS2
Revision 1.2
Order Number: A85874-002
38
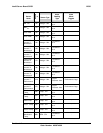
Table 23: Event Request Message Event Data Field Contents
Event
Trigger
Class
Event Data
Discrete 7:6 00 = Unspecified byte 2
01 = Previous state and/or severity in byte 2
10 = OEM code in byte 2
11 = Sensor specific event extension code in byte 2
5:4 00 = Unspecified byte 3
01 = Reserved
10 = OEM code in byte 3
11 = Sensor specific event extension code in byte 3
3:0 Offset from Event Trigger for discrete event state
Event Data 2
7:4 Optional offset from ‘Severity’ Event Trigger. (0Fh if unspecified).
3:0 Optional offset from Event Trigger for previous discrete event state.
0Fh if unspecified.
6.2.3 SMI Handler
The SMI handler handles and logs system level events that are not visible to the server
management firmware. The SMI handler, even those that are normally considered to generate an
NMI, preprocesses all system errors. The SMI handler sends a command to the BMC to log the
event and provides the data to be logged, a Set NMI Source command to indicate BIOS as the
source of the NMI, and a BIOS LCD command to display the LCD and LED message(s). A
correctable memory error does not generate an SMI. Correctable and uncorrectable memory
errors are handled and logged by the BMC.
6.2.3.1 PCI Bus Error
The PCI bus defines two error pins, PERR# and SERR#, for reporting PCI parity errors and
system errors, respectively.
6.2.3.2 Intel
®
Pentium
®
III Processor Bus Error
In the case of irrecoverable errors on the host processor bus, proper execution of SMI handler
cannot be guaranteed and SMI handler cannot be relied upon to log such conditions. The BIOS
SMI handler records the error to the System Event Log only if the system has not experienced a
catastrophic failure that compromises the integrity of the SMI handler. The BIOS always enables
the error correction and detection capabilities of the processors by setting appropriate bits in
processor model specific register (MSR).