13
Main circuit terminals
1
WIRING
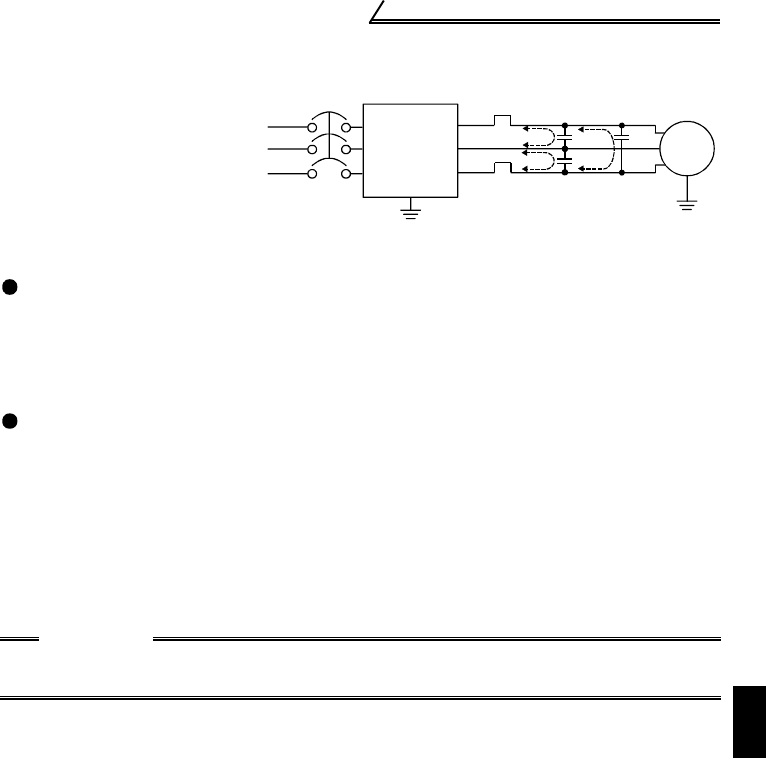
(2) Line-to-line leakage currents
Countermeasures
• Use the electronic thermal relay function of the inverter.
• Decrease the carrier frequency. Note that motor noise increases. Selection of
Soft-PWM (Pr. 70) makes it unoffending.
To ensure that the motor is protected against line-to-line leakage currents, it is
recommended to use a temperature sensor to directly detect motor temperature.
Installation and selection of no-fuse breaker
Install a no-fuse breaker (NFB) on the power receiving side to protect the wiring of
the inverter primary side. Select the NFB according to the power supply side power
factor (which depends on the power supply voltage, output frequency and load).
Especially for a completely electromagnetic NFB, one of a slightly large capacity
must be selected since its operation characteristic varies with harmonic currents.
(Check it in the data of the corresponding breaker.) As an ground leakage breaker,
use the Mitsubishi ground leakage breaker designed for harmonics and surge
suppression. (Refer to page 10 for the recommended models.)
Harmonics of
leakage currents
flowing in static
capacities between
the inverter output
cables may operate
the external thermal
relay unnecessarily.
CAUTION
•Select the NFB according to the inverter power supply capacity.
•Install one NFB per inverter.
Line-to-Line Leakage Current Path
Inverter
Power
supply
IM
Thermal relay
Line static
capacitances
NFB
Motor


















