Chapter 4. Port Routing | 61
ProSafe M4100 and M7100 Managed Switches
Port Routing Configuration
The M4100 and M7100 Managed Switch always supports Layer 2 bridging, but Layer 3
routing must be explicitly enabled, first for the M4100 and M7100 Managed Switch as a
whole, and then for each port that is to be part of the routed network.
The configuration commands used in the example in this section enable IP routing on ports
1/0/2,1/0/3, and 1/0/5.
The router ID will be set to the M4100 and M7100 Managed Switch’s
management IP address, or to that of any active router interface if the management address
is not configured.
After the routing configuration commands have been issued, the following functions will be
active:
• IP forwarding, responsible for forwarding received IP packets.
• ARP mapping, responsible for maintaining the
ARP Table used to correlate IP and MAC
addresses. The table contains both static entries and entries dynamically updated based
on information in received ARP frames.
• Routing
Table Object, responsible for maintaining the common routing table used by all
registered routing protocols.
You can then activate RIP or OSPF, used by routers to exchange route information, on top of
IP Routing. RIP is more often used in smaller networks, while OSPF was designed for larger
and more complex topologies.
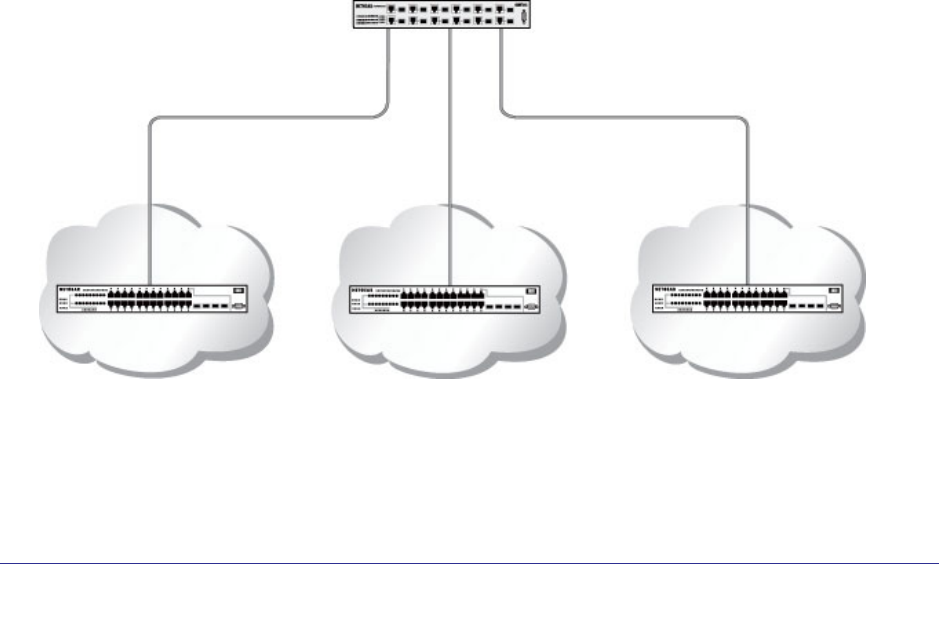
The following figure shows a Layer 3 switch configured for port routing. It connects three
dif
ferent subnets, each connected to a different port.
Subnet 2 Subnet 3 Subnet 5
Port 1/0/3
192.130.3.1
Port 1/0/5
192.64.4.1
Port 1/0/2
192.150.2.2
Layer 3 switch
acting as a router
Figure 7. Layer 3 switch configured for port routing


















