U
SING
RMON
9-2
RMON is designed to limit the amount of traffic required by management applications. It consists of an
independent agent that resides on the managed device, and is charged with monitoring and collecting information
about network traffic or the status of the host device. The agent gradually builds up information about the
attached segment or VLAN, storing this information in the relevant RMON database group. The client (or
management agent) then periodically communicates with the various RMON probes using SNMP protocol. It can
then present a numeric or graphic summary of the data collected from a large number of probes. However, if the
probe encounters a critical event (as defined by the management agent), it can automatically send a trap to the
management agent which will then respond to the event as determined by the Event Manager (see Chapter 8).
Starting the RMON Manager
To use the RMON Manager, open any network map and select the RMON program from the menu
bar. You can also run the RMON Manager directly from the Start Menu by selecting the RMON
Manager icon directly from the EliteView program group.
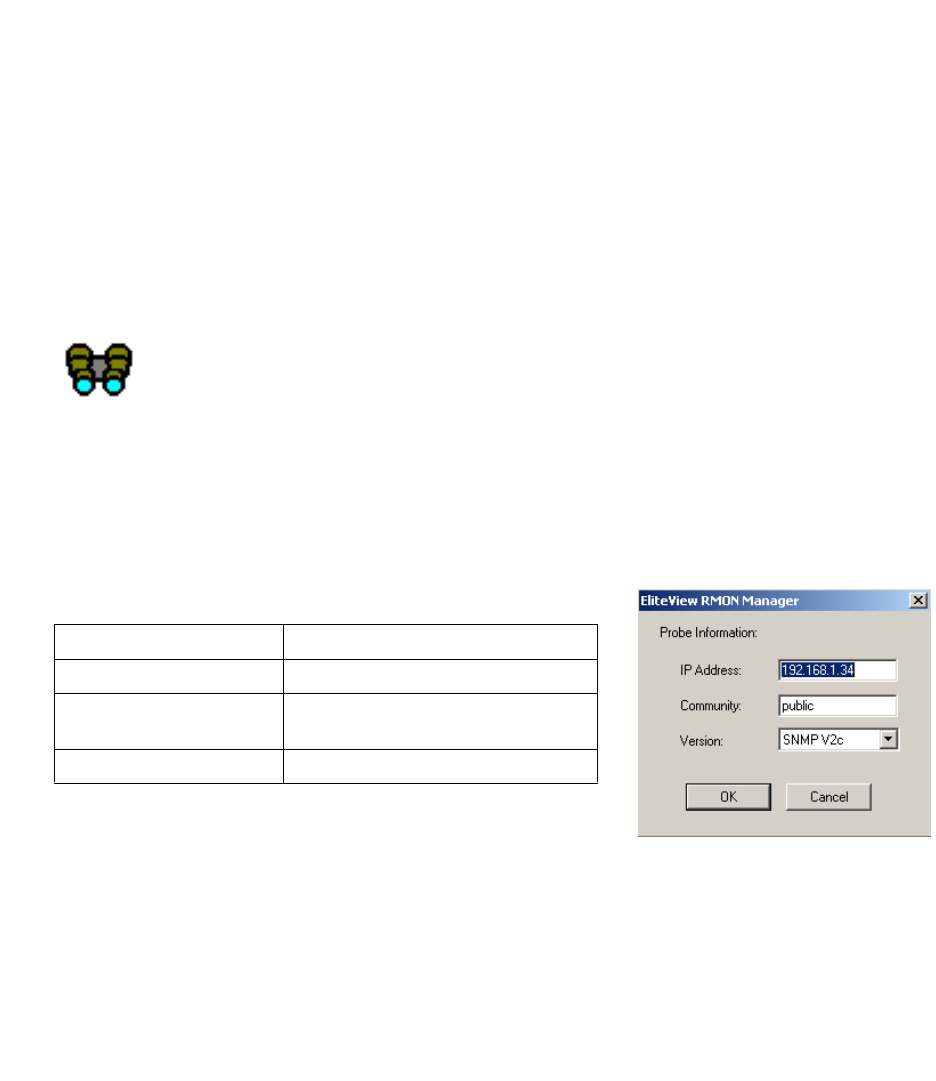
When you start the RMON Manager, a Probe Information window will pop up requesting target information. You
must provide the following information:
1. Enter the Target Address of the device.
2. Define a Community name describing the administrative relationship (i.e., access rights) between SNMP
entities.
If you open the main application for the RMON Manager, the screen will
display a detailed description of the managed device as shown in the
following example for a TigerSwitch SMC6724L3 1.
Table 9-1 RMON Manager Probe Window
Field Description
IP Address The IP Address of the RMON probe
Community The SNMP community in use by the
RMON Manager
Version Displays the SNMP Version


















