101
MSAP2000 AAM User’s Guide
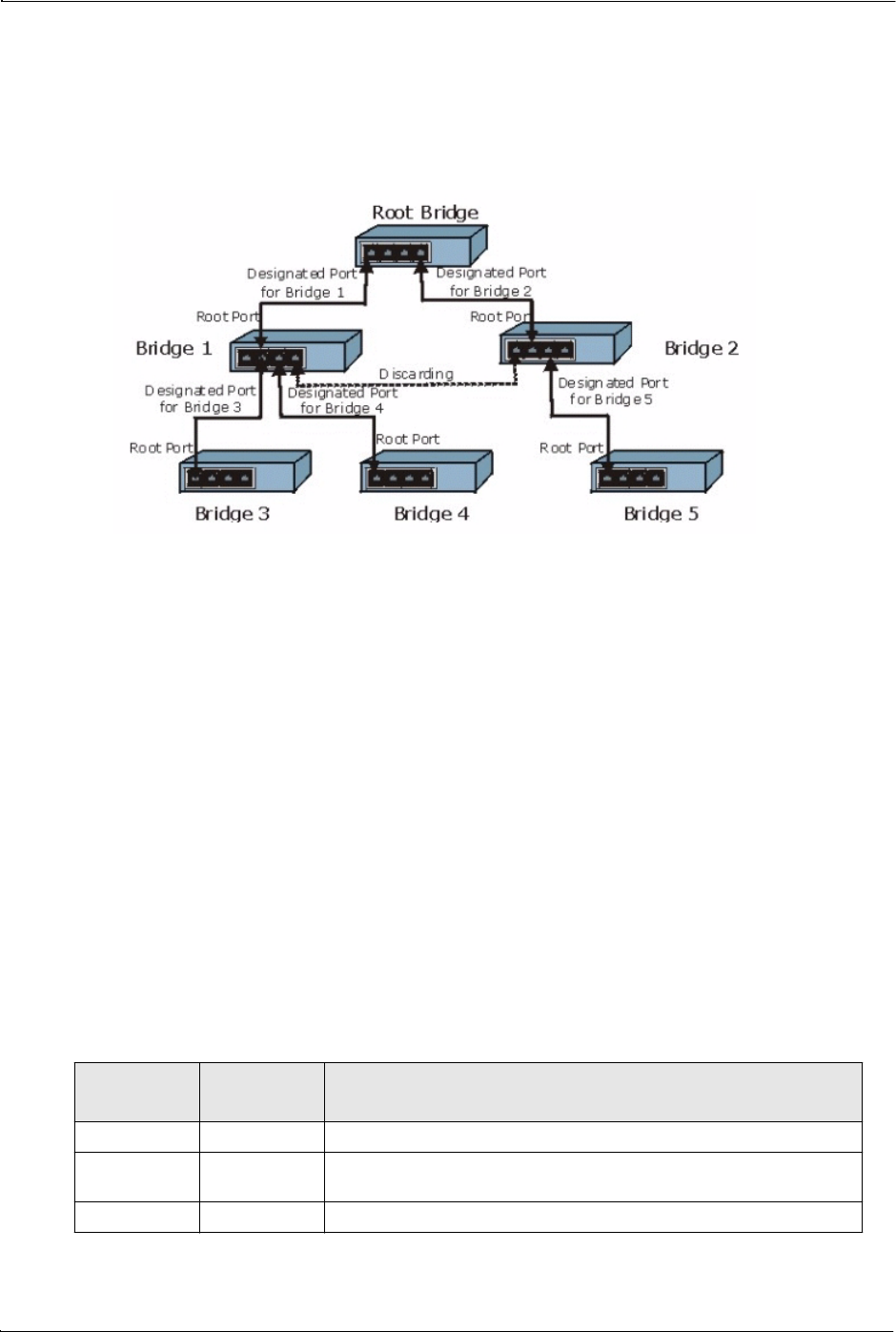
After a bridge determines the lowest cost-spanning tree with RSTP, it enables the
root port and the ports that are the designated ports for the connected LANs, and
disables all other ports that participate in RSTP. Network packets are therefore
only forwarded between enabled ports, eliminating any possible network loops.
Figure 45 STP Root Ports and Designated Ports
RSTP-aware devices exchange Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) periodically.
When the bridged LAN topology changes, a new spanning tree is constructed.
In RSTP, the devices send BPDUs every Hello Time. If an RSTP-aware device
does not get a Hello BPDU after three Hello Times pass (or the Max Age), the
device assumes that the link to the neighboring bridge is down. This device then
initiates negotiations with other devices to reconfigure the network to re-establish
a valid network topology.
In STP, once a stable network topology has been established, all devices listen
for Hello BPDUs transmitted from the root bridge. If an STP-aware device does
not get a Hello BPDU after a predefined interval (Max Age), the device assumes
that the link to the root bridge is down. This device then initiates negotiations with
other devices to reconfigure the network to re-establish a valid network topology.
RSTP assigns three port states to eliminate packet looping while STP assigns five
(see following table). A device port is not allowed to go directly from blocking state
to forwarding state so as to eliminate transient loops.
Table 34 RSTP Port States
RSTP PORT STP PORT DESCRIPTION
STATE STATE
Discarding Disabled STP is disabled (default).
Discarding Blocking Only configuration and management BPDUs are received and
processed.
Discarding Listening All BPDUs are received and processed


















