CN8000 User Manual
54
Note: 1. This policy operates on the device level. If Read Only is selected, the
device will only be able to be read – regardless of a user’s Read/Write
user account permissions.
2. If Read/Write is selected, the ability of a user to write depends on the
user’s Read/Write user account permissions.
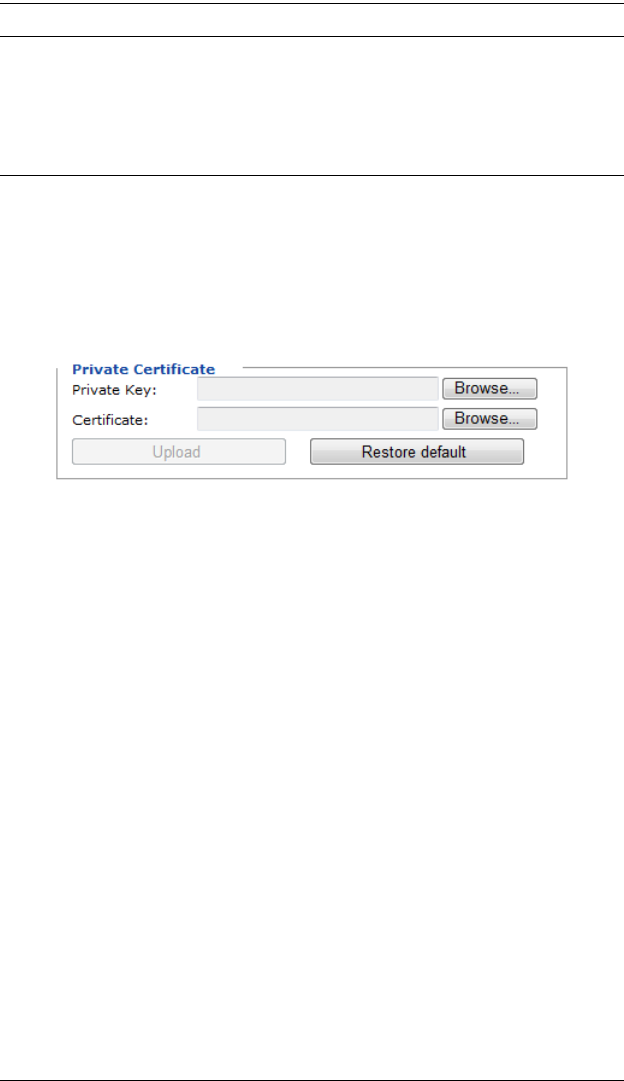
Private Certificate
When logging in over a secure (SSL) connection, a signed certificate is used to
verify that the user is logging in to the intended site. For enhanced security, the
Private Certificate section allows you to use your own private encryption key
and signed certificate, rather than the default ATEN certificate.
There are two methods for establishing your private certificate: generating a
self-signed certificate; and importing a third-party certificate authority (CA)
signed certificate.
Generating a Self-Signed Certificate
If you wish to create your own self-signed certificate, a free utility –
openssl.exe – is available for download over the web. See Self-Signed Private
Certificates, page 178 for details about using OpenSSL to generate your own
private key and SSL certificate.
Obtaining a CA Signed SSL Server Certificate
For the greatest security, we recommend using a third party certificate
authority (CA) signed certificate. To obtain a third party signed certificate, go
to a CA (Certificate Authority) website to apply for an SSL certificate. After
the CA sends you the certificate, save it to a convenient location on your
computer.
Importing the Private Certificate
To import the private certificate, do the following:
1. Click Browse to the right of Private Key; browse to where your private
encryption key file is located; and select it.
2. Click Browse to the right of Certificate; browse to where your certificate
file is located; and select it.
