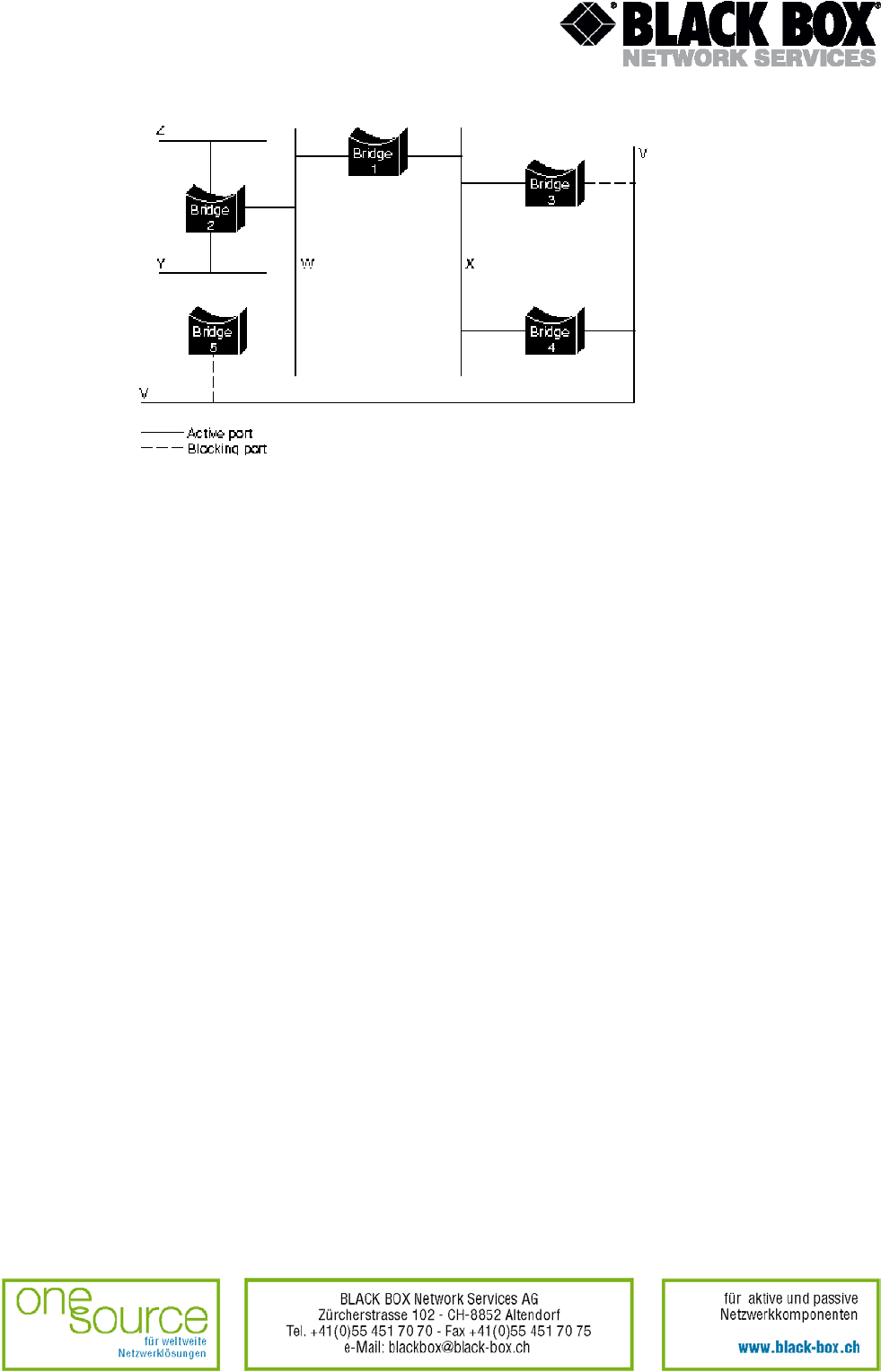
Fig. 5: Network after running STA
The spanning-tree calculation occurs when the bridge is powered up and whenever a topology
change is detected. The calculation requires communication between the spanning-tree bridges,
which is implemented through configuration messages. Configuration messages contain
information identifying the bridge that is assumed to be the root (root identifier) and the distance
from the sending bridge to the root bridge (root path cost) and also the bridge and port identifier
of the sending bridge and the age of information contained in the configuration message.
Bridges exchange configuration messages at regular intervals (typically 1–4 s). If a bridge fails
(causing a topology change), neighboring bridges will soon detect the lack of configuration
messages and initiate a spanning-tree recalculation.
The MDS92xxx-10BT device implements both transparent bridge and spanning tree algorithms.
4.2.4 Routing of networks
The word “routing” means forwarding information through an internetwork from source to
destination. At least one node must be passed when transmitting data. Routing is often
contrasted with bridging. The main difference between bridging and routing consists in the fact
that bridging occurs at the data link layer of the OSI reference model, while routing occurs at the
network layer. It means that routing and bridging use different information while moving it from
source to destination. It results in different way of implementing their tasks.
4.2.4.1 Routing components
Routing consists of two basic activities: determination of optimal routing paths between source
and destination and data transmission through network. The latter is called switching.
Version: 1.0 Page. 25 of 95


















