Switching
Switching algorithms are relatively simple and are basically the same for most routing protocols.
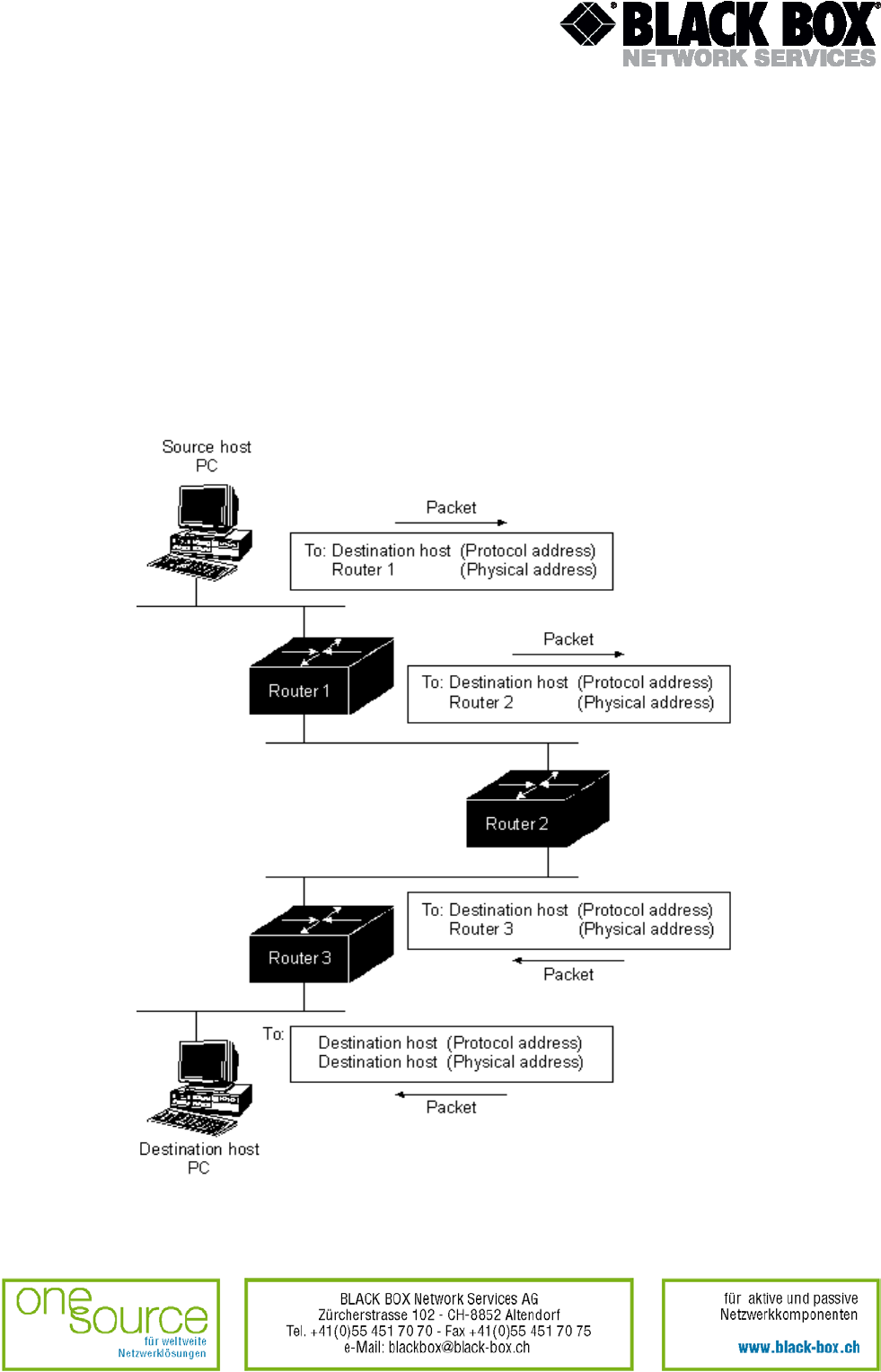
In most cases, a host determines the necessity of sending a packet to another host. Having
received a router's address, the source host sends a packet addressed specially to a router's
physical (MAC layer) address, however, the packet contains (network-layer) protocol address of
the destination host.
After checking the packet's destination protocol address, the router determines whether the
destination address is in the routing table. If the router did not find the address in the routing
table, it typically drops the packet. If the router knows where to forward the packet, it changes the
destination physical address to that of the next hop and transmits the packet.
During the packet transmission through an internetwork, its physical address changes, however,
the address of the network-layer protocol remains unchanged. Fig. 6 illustrates this process.
Fig. 6 Change of packet addresses
Version: 1.0 Page. 27 of 95


















