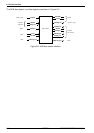
6: The Bus Interface
ARM720T CORE CPU MANUAL EPSON 6-7
6.4 Address and control signals
The address and control signals are described in the following sections:
•
HADDR[31:0]
•
HWRITE
•
HSIZE[2:0]
•
HBURST[2:0]
on page 6-8
•
HPROT[3:0]
on page 6-8.
6.4.1 HADDR[31:0]
HADDR[31:0] is the 32-bit address bus that specifies the address for the transfer. All
addresses are byte addresses, so a burst of word accesses results in the address bus
incrementing by four for each cycle.
The address bus provides 4GB of linear addressing space. This means that:
• when a word access is signalled, the memory system must ignore the bottom two
bits, HADDR[1:0]
• when a halfword access is signalled the memory system must ignore the bottom bit,
HADDR[0].
6.4.2 HWRITE
HWRITE specifies the direction of the transfer as follows:
HWRITE HIGH Indicates an ARM720T processor write cycle.
HWRITE LOW Indicates an ARM720T processor read cycle.
A burst of S cycles is always either a read burst or a write burst. The direction cannot be
changed in the middle of a burst.
6.4.3 HSIZE[2:0]
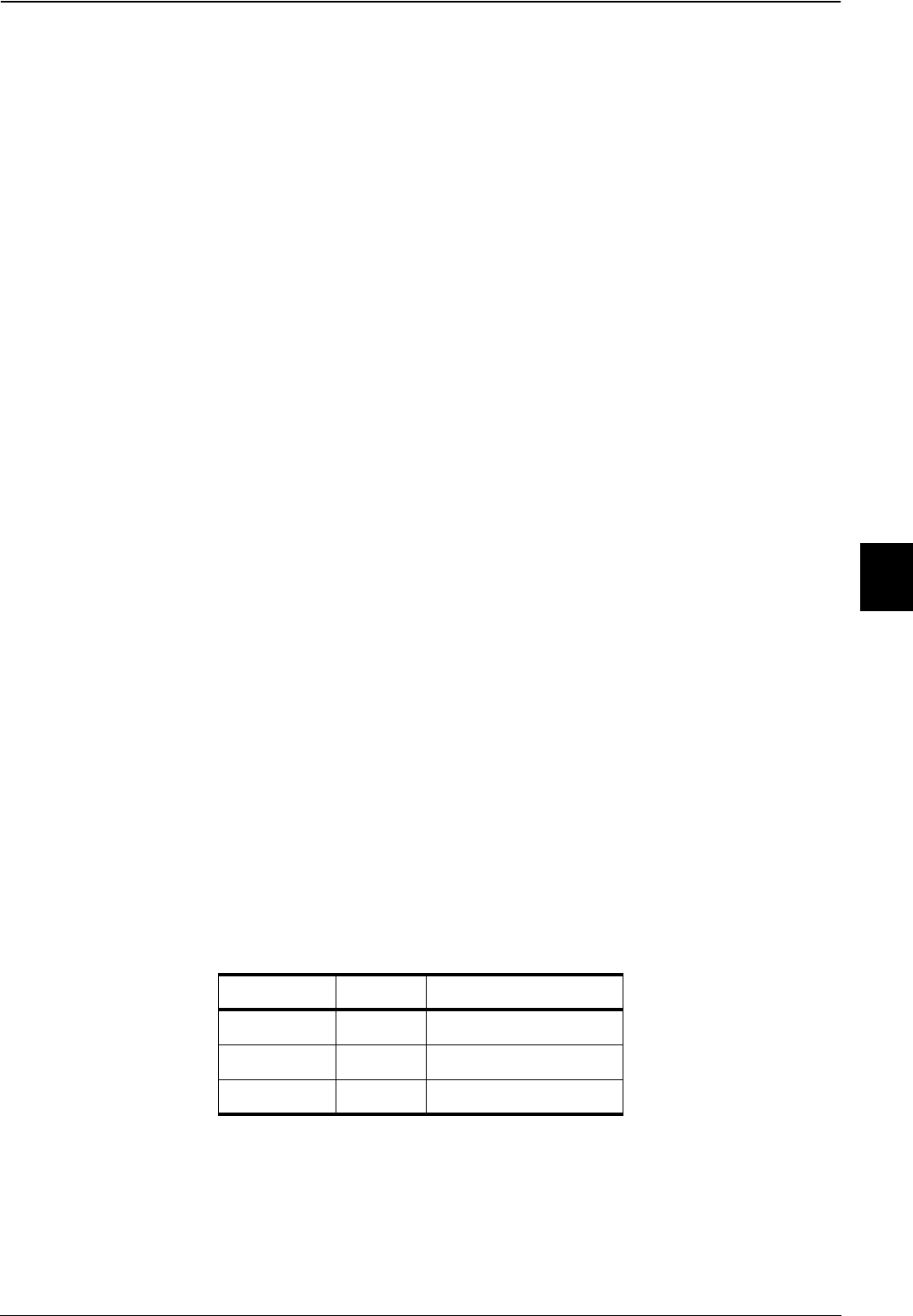
The SIZE[2:0] bus encodes the size of the transfer. The ARM720T processor can transfer word,
halfword, and byte quantities. This is encoded on SIZE[2:0] as shown in Table 6-2.
Note: To use the C compiler and the ARM debug tool chain, your system must support the
writing of arbitrary bytes and halfwords. You must provide write enables down to
the level of every individual byte to ensure support for all possible transfer sizes,
up to the bus width.
Table 6-2 Transfer size encodings
HSIZE[2:0] Size Transfer width
b000 8 bits Byte
b001 16 bits Halfword
b010 32 bits Word