Motherboard Layout and Routing Guidelines
2-14
Intel
®
440GX AGPset Design Guide
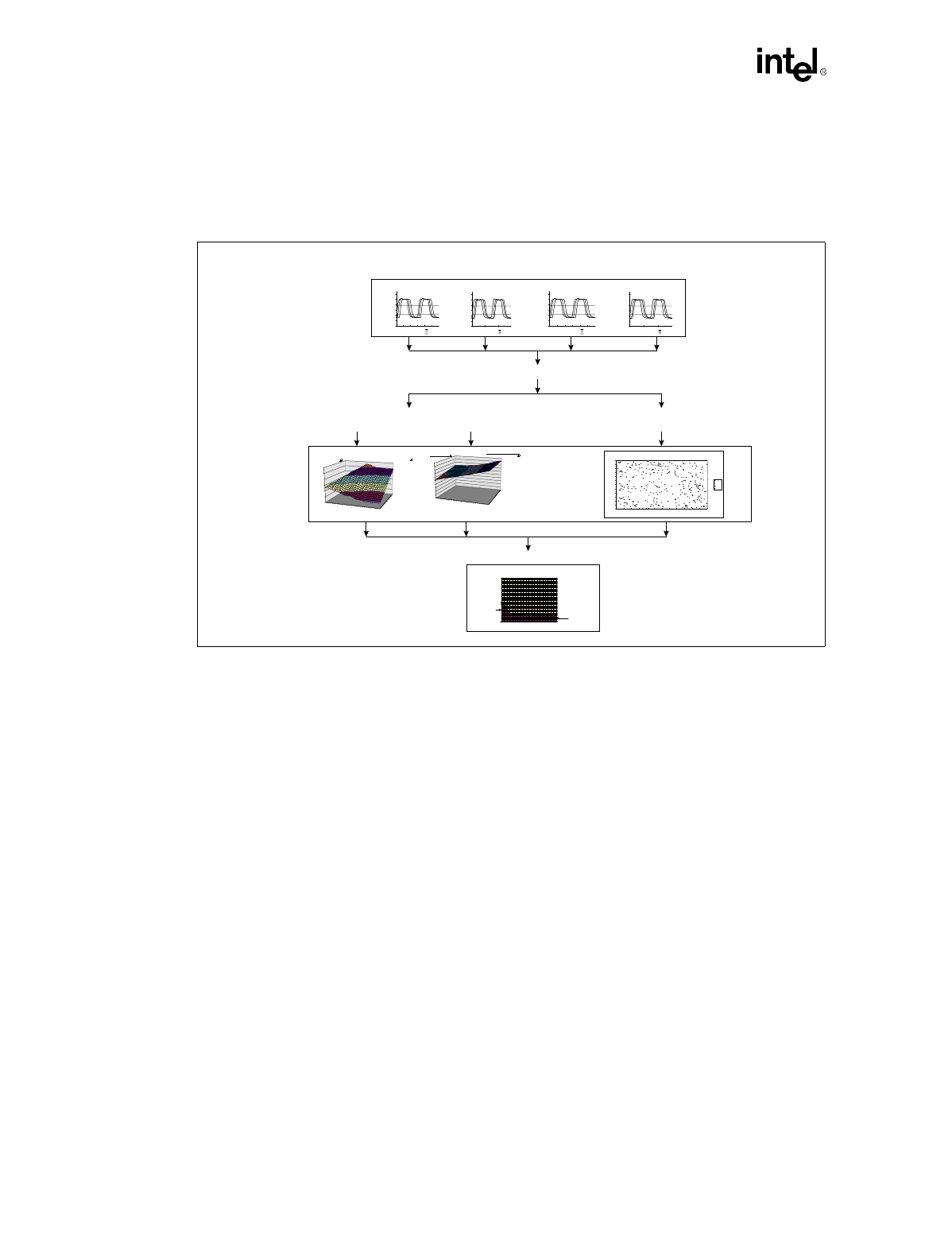
The methodology that Intel recommends is known as “Sensitivity Analysis”. In sensitivity analysis,
interconnect parameters are varied to understand how they affect system timing and signal
integrity. Sensitivity analysis can be further broken into two types of analysis, parametric sweeps
and Monte Carlo analysis, which are described below.
2.4 Placement & Layout
Once the pre-layout simulation is completed, route the board using the solution space resulting
from the sensitivity analysis.
2.5 Post-Layout Simulation
Following layout, extract the traces and run simulations to verify that the layout meets timing and
noise requirements. A small amount of trace “tuning” may be required, but experience at Intel has
shown that sensitivity analysis dramatically reduces the amount of tuning required.
The post layout simulations should take into account the expected variation for all interconnect
parameters. For timing simulations, use a V
REF
of 2/3 VTT ± 2% for both the Intel
®
Pentium
®
II
processor and Intel
®
440GX AGPset components. Flight times measured from the Pentium II
processor edge fingers to other system components use the standard flight time method.
Figure 2-13. Pre-layout simulation process
1
1.75
2.5
3.25
4
4.75
5.5
6.25
7
7.75
8.5
9.25
10
10.75
11.5
1
1.25
1.5
1.75
2
2.25
2.5
2.75
3
3.25
3.5
3.75
4
4.25
4.5
4.75
5
5.25
5.5
5.75
6
-101
L1
PCard#1 to 82440FX Separation Distance (in)
L2
PCar d#2 to 82440F X Se
p
aration Dist ance
(
in
)
DUAL KLAMA TH PROCE SSOR CARD SOL UTION SPACE
Rt = 56
Ω
+/- 5%
Solution space
MAX Fli
g
ht Time
LPC = 2.51 inches
LFX = 1 .5 inches
LRT = 1.5 inches
MIN Fli
g
ht Ti me
LPC = 0.44 inches
LFX = 0 .0 inches
LRT = 1.5 inches
Villations caused b
y
maximum fli
g
ht time
Villations caused b
y
minimum fli
g
ht time
1
1.75
2.5
3.25
4
4.75
5.5
6.25
7
7.75
8.5
9.25
10
10.75
11.5
1
1.75
2.5
3.25
4
4.75
5.5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
L1
PCar d#1 t o 8244 0FX Se
p
arati on Distanc e
(
in
)
L2
PCar d#2 t o 8244 0FX
Se
p
aratio n Dis tance
(
in
)
DUAL KLAMATH FLIGHT TIME
MAX FT
LPC = 2.51 inch es
LFX = 1.5 inches
LRT = 1.5 inches
Rt = 53.5 ohms
MIN FT
LPC = 0.44 inch es
LFX = 0.0 inches
LRT = 1.5 inches
Rt = 53.5 ohms
82440FX to KLAMATH MIN FT RISING (fast silicon - fast board)
1
1.75
2.5
3.25
4
4.75
5.5
6.25
7
7.75
8.5
9.25
10
10.75
11.5
1
1.75
2.5
3.25
4
4.75
5.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
3.5
4
4.5
5
L1
PCard#1 to 8244 0FX Se
p
aratio n Dista nce
(
in
)
L2
PCard#2 to 8244 0FX
Se
p
aratio n Distance
(
in
)
DUAL KLAMATH FLIGHT TIME
MAX FT
LPC = 2 .51 in ches
LFX = 1.5 inches
LRT = 1.5 inches
Rt = 5 8.5 ohm s
MIN FT
LPC = 0 .44 in ches
LFX = 0.0 inches
LRT = 1.5 inches
Rt = 5 8.5 ohm s
82440F X to KLA MATH
MAX FT RISING (slow silicon - slow board)
DUAL KLAMATH PROCESSOR CARD SOLUTION SPACE
Monte Carlo
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
0123456789101112
PCard to 82440FX Sep aration Distance (in)
PCard to 82440FX Separation Distance (in)
Pas s
Pas s
Fail
Fail
Sensitivity Analyses
= KLAMATH1 X3
= KLAMATH1PIN X3
= KLAMATH2 X3
= KLAMATH2PIN X3
= 82440FXPIN 33
= ALL OTHERS= ALL OTHERS
0.25v
0.75v
1.25v
1.75v
0.00ns 20.00ns 40.00ns
X = 0.00ns y = +0.000v xdelta = 0.000ns
NET: SLOWDPNM_LS_12_6, DRIVER: KLAMATH1 TRACKING: KLAMATH1 X3
= KLAMATH1 X3
= KLAMATH1PIN X3
= KLAMATH2 X3
= KLAMATH2PIN X3
= 82440FXPIN 33
= ALL OTHERS= ALL OTHERS
0.25v
0.75v
1.25v
1.75v
0.00ns 20.00ns 40.00ns
X = 0.00ns y = +0.000v xdelta = 0.000ns
NET: SLOWDPNM_LS_12_6, DRIVER: KLAMATH2 TRACKING: KLAMATH1 X3
= KLAMATH1 X3
= KLAMATH1PIN X3
= KLAMATH2 X3
= KLAMATH2PIN X3
= 82440FXPIN 33
= ALL OTHERS= ALL OTHERS
0.25v
0.75v
1.25v
1.75v
0.00ns 20.00ns 40.00ns
X = 0.00ns y = +0.000v xdelta = 0.000ns
NET: SLOWDPNM_LS_12_6, DRIVER: KLAMATH1 TRACKING: KLAMATH1 X3
= KLAMATH1 X3
= KLAMATH1PIN X3
= KLAMATH2 X3
= KLAMATH2PIN X3
= 82440FXPIN 33
= ALL OTHERS= ALL OTHERS
0.25v
0.75v
1.25v
1.75v
0.00ns 20.00ns 40.00ns
X = 0.00ns y = +0.000v xdelta = 0.000ns
NET: SLOWDPNM_LS_12_6, DRIVER: KLAMATH2 TRACKING: KLAMATH1 X3
Interconnect Simulations (Transmission-Line)
Performance as function of Length
(flight time, signal quality, etc.)
Monte Carlo
(pass/fail as function of length)
Solution Space


















