2: Introduction
WiBox® 2100E Device Server User Guide 14
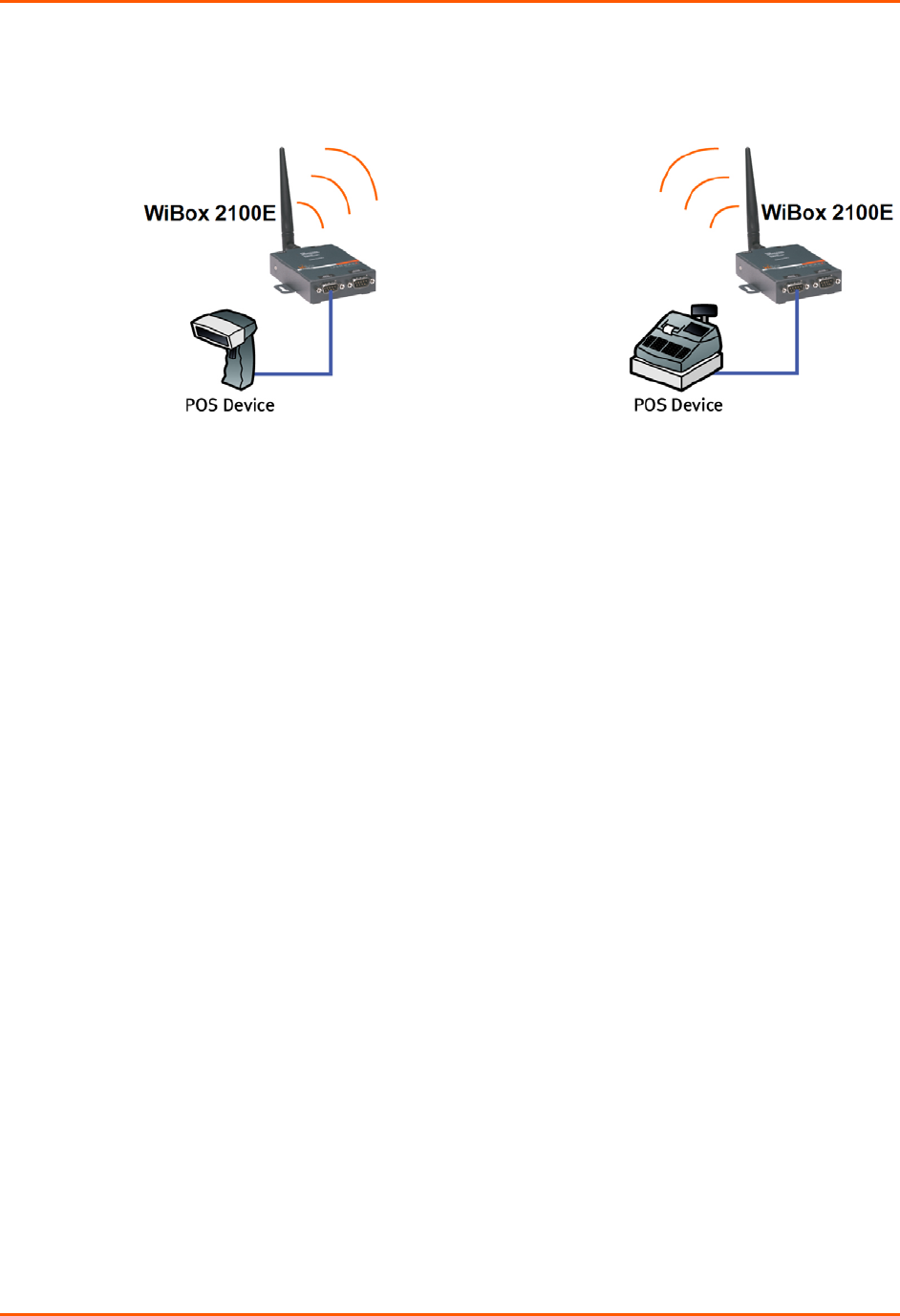
Ad Hoc WiBox 2100E Connection
Figure 2-4. Direct WiBox 2100E-to-WiBox 2100E Connection
In the example above, the two WiBox 2100E devices have established an Ad Hoc peer-to-peer
relationship. They communicate directly to each other’s serial devices without a PC or an AP.
WiBox 2100E with Ethernet
With this model, you can select either a wireless or an Ethernet connection.
Protocol Support
The WiBox 2100E device server uses the TCP/IP protocol stack for network communications.
Other supported protocols include:
ARP, UDP, TCP, ICMP, Telnet, TFTP, AutoIP, DHCP, HTTP, and SNMP for network
communications and management.
TCP, UDP, and Telnet for connections to the serial port.
TFTP for firmware and web page updates.
IP for addressing, routing, and data block handling over the network.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) for typical datagram applications in which devices interact
with other devices without maintaining a point-to-point connection.
Configuration Methods
After the physical installation of the WiBox 2100E, configuration is required. For the unit to
operate correctly on a network, it must have:
A unique IP address
Appropriate settings for network communications
Methods for logging into the device server and assigning IP addresses (as well as setting other
configurable parameters) include:
Web Manager: Through a web interface, configure the WiBox 2100E and its settings using the
WiBox 2100E’s Web Manager. (See 4: Web Manager Configuration.)


















