Chapter 2 Data Replication
13
2
2
2
.
.
.
3
3
3
.
.
.
1
1
1
R
R
R
e
e
e
p
p
p
l
l
l
i
i
i
c
c
c
a
a
a
t
t
t
e
e
e
a
a
a
n
n
n
d
d
d
S
S
S
t
t
t
a
a
a
t
t
t
e
e
e
T
T
T
r
r
r
a
a
a
n
n
n
s
s
s
i
i
i
t
t
t
i
i
i
o
o
o
n
n
n
s
s
s
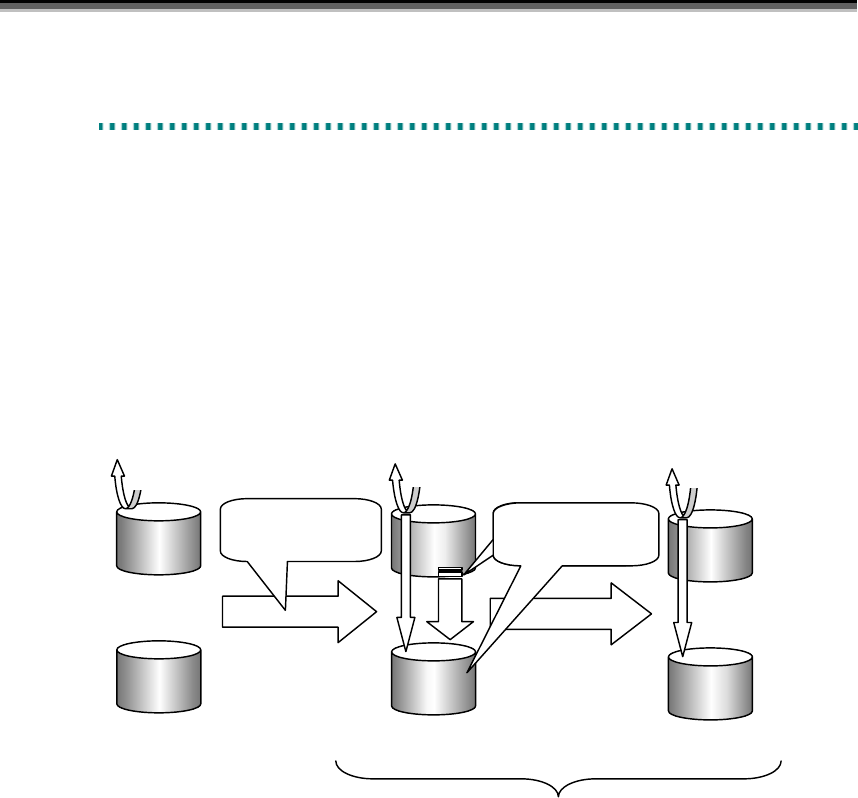
When Replicate is performed, data copy from MV to RV starts to reflect the content of MV to RV.
Any update to MV after Replicate is also reflected to RV.
After Replicate is started, the difference between MV and RV gradually decreases, and eventually the
content of MV at the beginning of Replicate is completely reflected to RV (The difference is zero).
The state from the beginning of Replicate to the content of MV is completely reflected to RV is called
the “Replicate execution”. The state where the difference between MV and RV is zero is called the
state synchronized by Replicate, or simply the “synchronous state“. Replicate execution and the state
synchronized by Replicate are collectively called the Replicate state.
Synchronous Execution
Replicate State
Figure 2-3 Replicate and State Transitions
MV
RV
Separate State
MV
RV
MV
RV
Synchronous State
Replicate
operation
starts
Update to MV
Update to MV
Update to MV
Until the
difference is zero


















