5-2 Reference Guide
Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX)
IPX is a datagram, connectionless protocol that Novell adapted from
Xerox Network System’s (XNS) Internet Datagram Protocol (IDP). IPX
is dynamically routed, and the routing architecture works by
“learning” network addressing automatically.
IPX address
An IPX address consists of a network number, a node number, and a
socket number. An IPX network number is composed of eight
hexadecimal digits. The network number must be the same for all
nodes on a particular physical network segment. The node number
is composed of twelve hexadecimal digits and is usually the
hardware address of the interface card. The node number must be
unique inside the particular IPX network. Socket numbers
correspond to the particular service being accessed.
Socket
A socket in IPX is the equivalent of a port in TCP/IP. Sockets route
packets to different processes within a single node. Novell has
reserved several sockets for use in the NetWare environment:
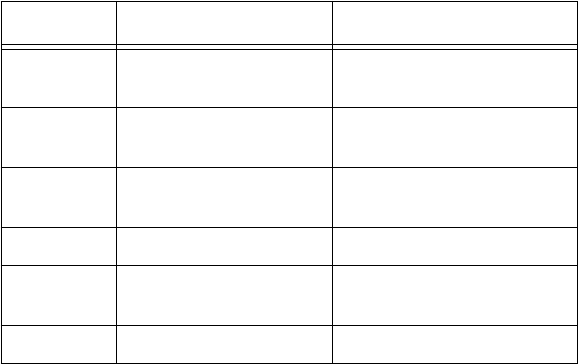
Field Value Packet Type Description
00h Unknown Packet Type Used for all packets not
classified by any other type
01h Routing Information
Packet
Unused for RIP packets
04h Service Advertising
Packet
Used for SAP packets
05h Sequenced Packet Used for SPX packets
11h NetWare Core Protocol
Packet
Used for NCP packets
14h Propagated Packet Used for Novell NetBIOS


















