7-8 Reference Guide
For example, let’s say the first inspector’s orders are to send along
all packages that come from Rome, and the second inspector’s
orders are to reject all packages that come from France. If a
package arrives from Rome, the first inspector sends it along
without allowing the second inspector to see it. A package from
Paris is ignored by the first inspector, rejected by the second
inspector, and never seen by the others. A package from London is
ignored by the first two inspectors, and so it’s seen by the third
inspector.
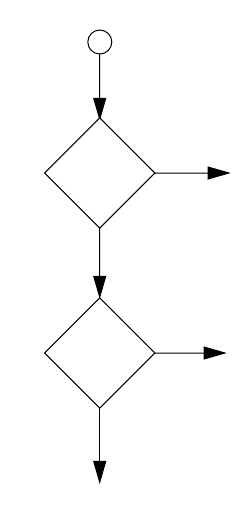
In the same way, filter sets apply their filters in a particular order.
The first filter applied can pass or discard a packet before that
packet ever reaches any of the other filters. If the first filter can
neither pass nor discard the packet (because it cannot match any
criteria), the second filter has a chance to pass or reject it, and so
on. Because of this hierarchical structure, each filter is said to have
a priority. The first filter has the highest priority, and the last filter
has the lowest priority.
Using filter sets
You use filter sets by linking them to particular connection profiles
and the answer profile. When you create a connection profile or edit
the answer profile, you can specify a filter set for that profile to use.
To learn how to link a filter set to a connection profile, see “Adding a
Connection Profile” on page 2-16 or “Changing a Connection
Profile” on page 2-15.
To learn how to link a filter set to the answer profile, see “How the
default profile works for a permanent circuit” on page 2-45, or “How
the default profile works for a permanent circuit” on page 2-45.
packet
first
filter
match?
yes
pass or
discard?
to network
discard
(delete)
pass
no
to next
filter
send


















