www.ti.com
1.4IndustryStandard(s)ComplianceStatement
2PeripheralArchitecture
2.1ClockControl
2.2MemoryMap
2.3SignalDescriptions
PeripheralArchitecture
TheEMACperipheralconformstotheIEEE802.3standard,describingtheCarrierSenseMultipleAccess
withCollisionDetection(CSMA/CD)AccessMethodandPhysicalLayerspecifications.TheIEEE802.3
standardhasalsobeenadoptedbyISO/IECandre-designatedasISO/IEC8802-3:2000(E).
Indifferencefromthisstandard,theEMACperipheraldoesnotusetheTransmitCodingErrorsignal
MTXER.Insteadofdrivingtheerrorpinwhenanunderflowconditionoccursonatransmittedframe,the
EMACintentionallygeneratesanincorrectchecksumbyinvertingtheframeCRC,sothatthetransmitted
frameisdetectedasanerrorbythenetwork.
ThissectiondiscussesthearchitectureandbasicfunctionoftheEMACperipheral.
ThefrequenciesforthetransmitandreceiveclocksarefixedbytheIEEE802.3specificationas:
•2.5MHZat10Mbps
•25MHZat100Mbps
AllEMAClogicisclockedsynchronouslywiththePLL1/6peripheralclock,exceptfortheEthernetMII
synchronizationlogic.
ThetransmitandreceiveclocksourcesareprovidedfromtheexternalPHYviatheMTCLKandMRCLK
pins.TheseclocksareinputstotheEMACmoduleandoperateat2.5MHZin10-Mbpsmode,andat25
MHZin100-Mbpsmode.Fortimingpurposes,dataistransmittedandreceivedwithrespecttoMTCLK
andMRCLK,respectively.
TheMDIOclockisbasedonadivide-downoftheperipheralclock(PLL1/6)specifiedtorunupto2.5
MHZ,althoughtypicaloperationwouldbe1.0MHZ.Sincetheperipheralclockfrequencyisvariable
(PLL1/6),theapplicationsoftwareordrivercontrolsthedivide-downamount.
TheEMACperipheralincludesinternalmemorythatisusedtoholdinformationabouttheEthernet
packetsreceivedandtransmitted.ThisinternalRAMis2K×32bitsinsize.Datacanbewrittentoand
readfromtheEMACinternalmemorybyeithertheEMACortheCPU.Itisusedtostorebufferdescriptors
thatare4-words(16-bytes)deep.This8Klocalmemoryholdsenoughinformationtotransferupto512
EthernetpacketswithoutCPUintervention.
Thepacketbufferdescriptorscanalsobeplacedintheinternalprocessormemory(L2),orinEMIF
memory(DDR).Therearesometradeoffsintermsofcacheperformanceandthroughputwhen
descriptorsareplacedinthesystemmemory,versuswhentheyareplacedintheEMAC’sinternal
memory.Cacheperformanceisimprovedwhenthebufferdescriptorsareplacedininternalmemory.
However,theEMACthroughputisbetterwhenthedescriptorsareplacedinthelocalEMACRAM.
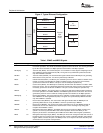
Figure2showsadevicewithintegratedEMACandMDIOinterfacedviaaMIIconnectioninatypical
system.TheEMACmoduledoesnotincludeatransmiterror(MTXER)pin.Inthecaseoftransmiterror,
CRCinversionisusedtonegatethevalidityofthetransmittedframe.
TheindividualEMACandMDIOsignalsfortheMIIinterfacearesummarizedinTable1.Formore
information,refertoeithertheIEEE802.3standardorISO/IEC8802-3:2000(E).
SPRU941A–April2007EthernetMediaAccessController(EMAC)/13
ManagementDataInput/Output(MDIO)
SubmitDocumentationFeedback