ZyWALL USG 100/200 Series User’s Guide
513
CHAPTER 30
ADP
30.1 Overview
This chapter introduces ADP (Anomaly Detection and Prevention), anomaly profiles and
applying an ADP profile to a traffic direction. ADP protects against anomalies based on
violations of protocol standards (RFCs – Requests for Comments) and abnormal flows such as
port scans.
30.1.1 ADP and IDP Comparison
1 ADP anomaly detection is in general effective against abnormal behavior while IDP
packet inspection signatures are in general effective for known attacks (see Chapter 29
on page 483 for information on packet inspection).
2 ADP traffic and anomaly rules are updated when you upload new firmware. This is
different from the IDP packet inspection signatures and the system protect signatures
you download from myZyXEL.com.
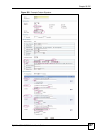
30.1.2 What You Can Do Using the ADP Screens
•Use Anti-X > ADP > General (Section 30.2 on page 514) to turn anomaly detection on or
off and apply anomaly profiles to traffic directions.
•Use Anti-X > ADP > Profile (Section 30.3 on page 516) to add a new profile, edit an
existing profile or delete an existing profile.
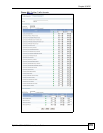
30.1.3 What You Need To Know About ADP
Traffic Anomalies
Traffic anomaly rules look for abnormal behavior or events such as port scanning, sweeping or
network flooding. It operates at OSI layer-2 and layer-3. Traffic anomaly rules may be
updated when you upload new firmware.
Protocol Anomalies
Protocol anomalies are packets that do not comply with the relevant RFC (Request For
Comments). Protocol anomaly detection includes HTTP Inspection, TCP Decoder, UDP
Decoder and ICMP Decoder. Protocol anomaly rules may be updated when you upload new
firmware.