BGP Overview Configuring BGP
page 4-12 OmniSwitch 6800/6850/9000 Advanced Routing Configuration Guide December 2007
Policies
Routing policies enable route classification for importing and exporting routes. The goal of routing
policies is to control traffic flow. Policies can be applied to egress and ingress traffic.
Note. Policies can be applied only to IPv4 routes and not to IPv6 prefixes.
Policies act as filters to either permit or deny specified routes that are being learned or advertised from a
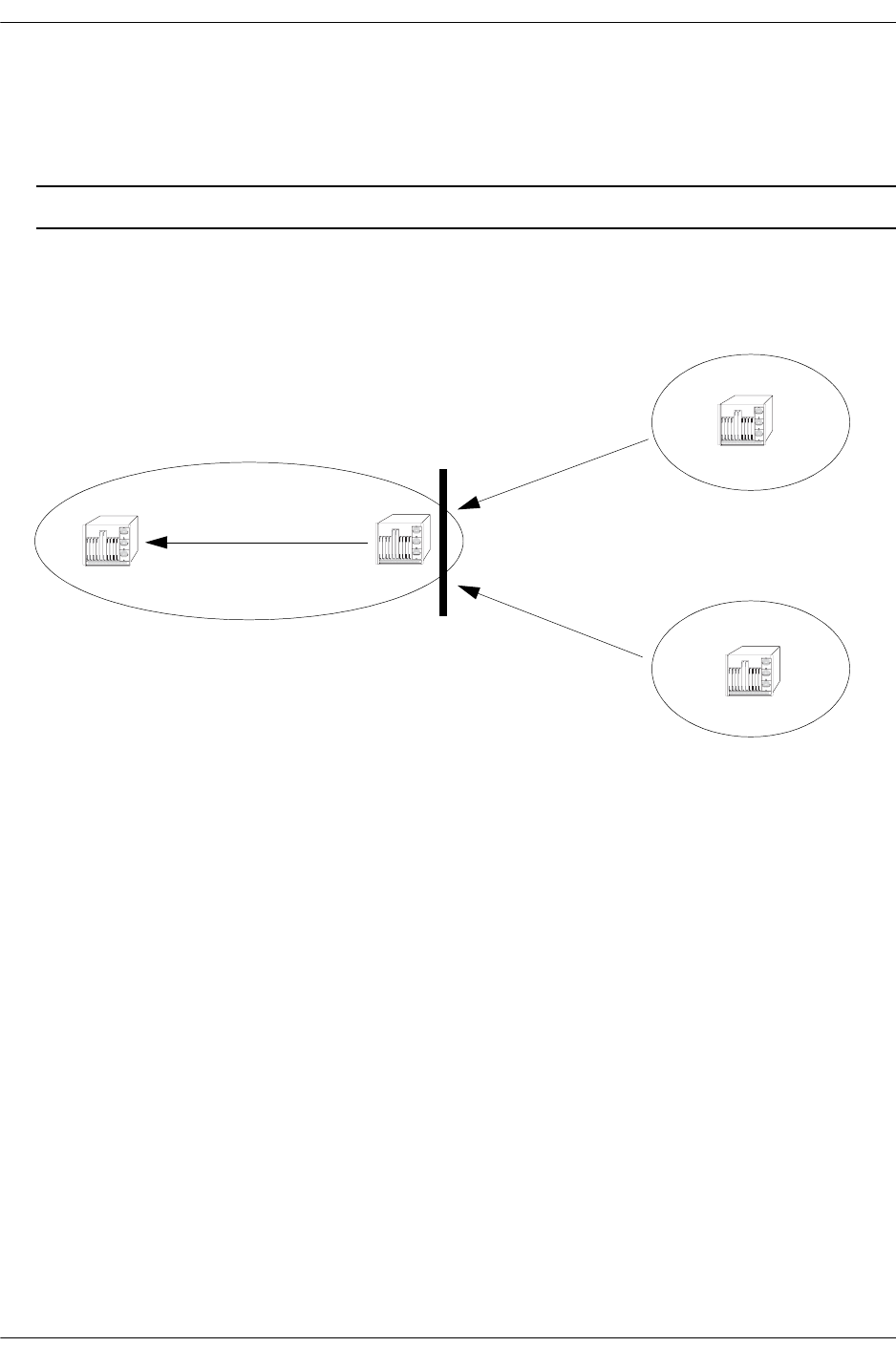
peer. The following diagram demonstrates this concept:
Routes from AS 200 and AS 300 are being learned by AS 100. However, there is an incoming AS Path
policy at the edge of AS 100 that prevents routes that originate in AS 300 from being propagated through-
out AS 100.
There are four main policy types:
• AS Path. This policy filters routes based on AS path lists. An AS path list notes all of the ASs the route
travels to reach its destination.
• Community Lists. Community list policies filter routes based on the community to which a route
belongs. Communities can affect route behavior based on the definition of the community.
• Prefix Lists. Prefix list policies filter routes based on a specific network address, or a range of network
addresses.
• Route Maps. Route map policies filter routes by amalgamating other policies into one policy. It is a
way of combining many different filter options into one policy.
Creating and assigning policies is discussed in “Routing Policies” on page 4-45.
AS 100
AS 200
AS 300
Incoming policy
(deny AS 300)
Route 1
Route 2
Route 1


















