PIM Overview Configuring PIM
page 7-8 OmniSwitch 6800/6850/9000 Advanced Routing Configuration Guide December 2007
PIM Overview
Protocol-Independent Multicast (PIM) is an IP multicast routing protocol that uses routing information
provided by unicast routing protocols such as RIP and OSPF. Note that PIM is not dependent on any
particular unicast routing protocol.
Downstream routers must explicitly join PIM distribution trees in order to receive multicast streams on
behalf of receivers or other downstream PIM routers. This paradigm of receiver-initiated forwarding
makes PIM ideal for network environments where receiver groups are thinly populated and bandwidth
conservation is a concern, such as in wide area networks (WANs).
Note. OmniSwitch 6800/6850/9000 switches support PIM-DM and PIM-SMv2 are not compatible with
PIM-SMv1.
PIM-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM)
Sparse mode PIM (PIM-SM) contrasts with flood-and-prune dense mode multicast protocols, such as
DVMRP and PIM-Dense Mode (PIM-DM) in that multicast forwarding in PIM is initiated only via
specific requests, referred to as Join messages.
The following sections provide basic descriptions for key components used when configuring a PIM-SM
network. These components include the following:
• Rendezvous Points (RPs) and Candidate Rendezvous Points (C-RPs)
• Bootstrap Routers (BSRs) and Candidate Bootstrap Routers (C-BSRs)
• Designated Routers (DRs)
• Shared Trees, also referred to as Rendezvous Point Trees (RPTs)
• Avoiding Register Encapsulation
Rendezvous Points (RPs)
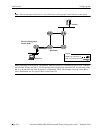
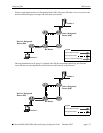
In PIM-SM, shared distribution trees are rooted at a common forwarding router termed a Rendezvous
Point (RP). The RP unencapsulates Register messages and forwards multicast packets natively down
established distribution trees to receivers. The resulting topology is referred to as the RP Tree (RPT).
For an illustrated example of an RPT and the RP’s role in a simple PIM-SM environment, refer to “Shared
(or RP) Trees” on page 7-9.
Candidate Rendezvous Points (C-RPs)
A Candidate Rendezvous Point (C-RP) is a PIM-enabled router that sends periodic C-RP advertisements
to the Bootstrap Router (BSR). When a BSR receives a C-RP advertisement, the BSR may include the C-
RP in its RP-set. For more information on the BSR and RP-set, refer to page 7-9.