PIM Overview Configuring PIM
page 7-14 OmniSwitch 6800/6850/9000 Advanced Routing Configuration Guide December 2007
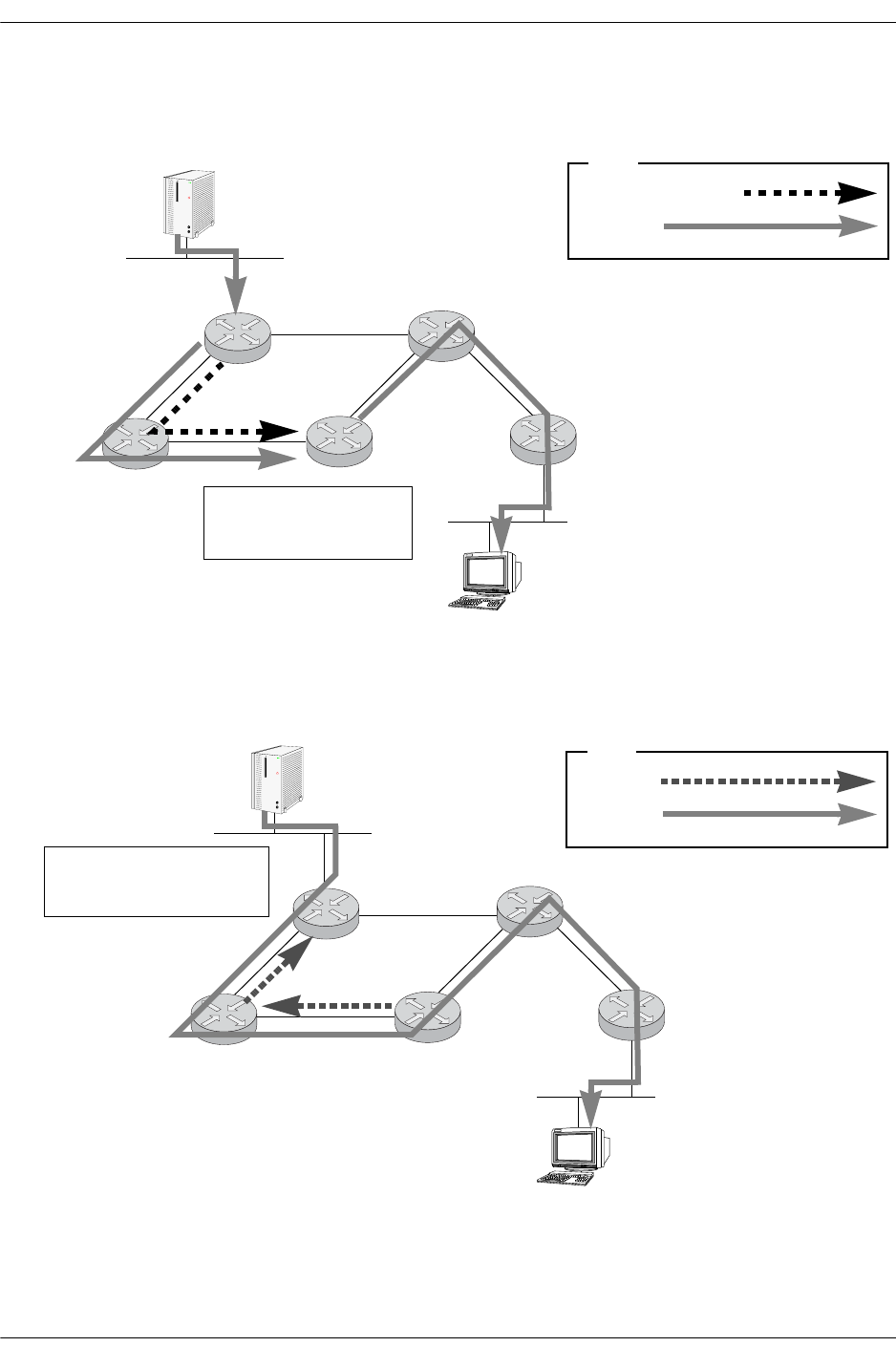
When the Sender’s DR receives the (S,G) Join, it sends data natively as well. When these data packets
arrive natively at the RP, the RP will be receiving two copies of each of these packets—one natively and
one encapsulated. The RP drops the register-encapsulated packets and forwards only the native packets.
A register-stop packet is sent back to the sender’s DR to prevent the DR from unnecessarily encapsulating
the packets. Once the register-encapsulated packets are discontinued, the packets flow natively from the
sender to the RP—along the source-specific tree to the RP and, from there, along the shared tree to all
receivers.
Because packets are still forwarded along the shared tree from the RP to all of the receivers, this does not
constitute a true Shortest Path Tree (SPT). For many receivers, the route via the RP may involve a signifi-
cant detour when compared with the shortest path from the source to the receivers.
Sender
Receiver
RP
DR
Legend
DR
Register-Encapsulated Traffic
Native Traffic
The RP receives both native and
encapsulated data. It drops the
encapsulated data and forwards only
the native packets.
Sender
Receiver
RP
DR
DR
Legend
Register-Stop
Native Traffic
Register-Stop Packet
The Sender’s DR stops sending register-
encapsulated packets once it receives
the Register-Stop packet. The DR now
sends only native traffic.