Hardware Configuration Features B-125
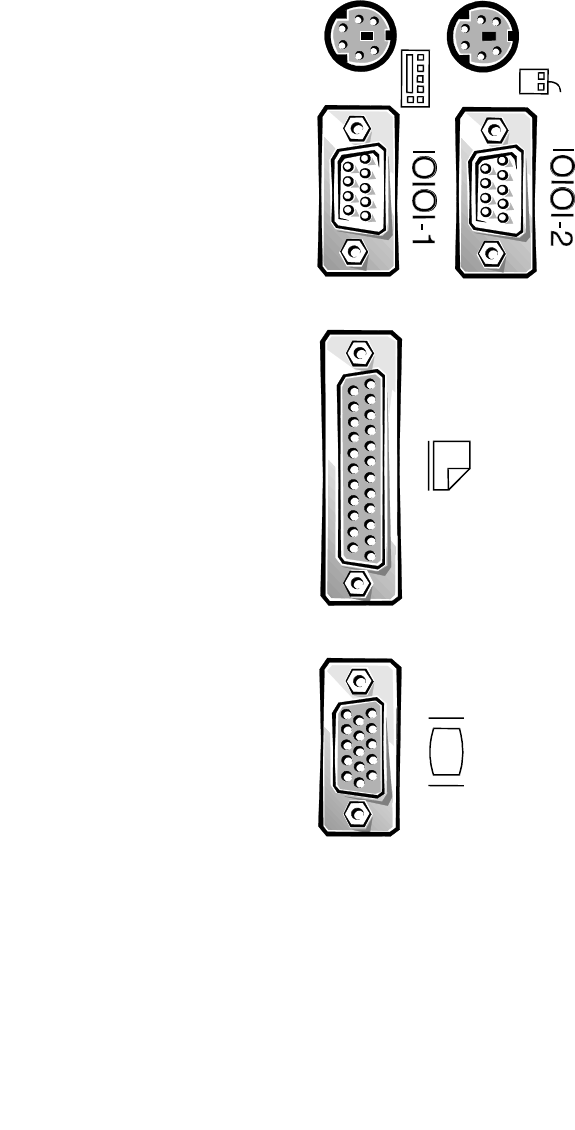
I/O Ports and Connectors
The I/O ports and connectors on the back panel of the
computer are the gateways through which the computer
system communicates with external devices, such as a
keyboard, mouse, printer, and monitor. Figure B-2 identi-
fies the I/O ports and connectors for your system.
Serial and Parallel Ports
The two built-in serial ports use 9-pin D-subminiature con-
nectors on the back panel. These ports support devices such as
external modems, printers, plotters, and mice that require serial
data transmission (the transmission of data one bit at a time
over one line).
Most software uses the term COM (for COMmunications)
plus a number to designate a serial port (for example, COM1
or COM2). The default designations of your computer’s built-
in serial ports are COM1 and COM2. COM1 is the bottom
connector; COM2 is on the top.
The built-in parallel port uses a 25-pin D-subminiature con-
nector on the computer’s back panel. This I/O port sends data
in parallel format (where eight data bits, or one byte, are sent
simultaneously over eight separate lines in a single cable). The
parallel port is used primarily for printers.
Most software uses the term LPT (for Line PrinTer) plus a
number to designate a parallel port (for example, LPT1). The
default designation of the computer’s built-in parallel port is
LPT1.
Port designations are used, for example, in software
installation procedures that include a step in which you
identify the port to which a printer is attached, thus tell-
ing the software where to send its output. (An incorrect
designation prevents the printer from printing or causes
scrambled print.)
Figure B-2. I/O Ports and Connectors
KYBD (left)
MOUSE (right)
SERIAL
COM 1(left)
SERIAL
COM 2 (right)
PARALLEL
LPT 1
VIDEO
JVGA


















