Intel® NetStructure™ ZT 8101 10/100 Ethernet Switch User’s Manual 29
Switch Management and Operating Concepts
Priority
The ZT 8101 switch allows you to assign specific levels of priority to traffic traversing the switch.
Setting priority allows you to protect bandwidth for important nodes on your network. Traffic in
the switch can be prioritized any of the following ways:
• MAC Address
• TCP/IP address
• Physical Port
• 802.1p Priority Bits
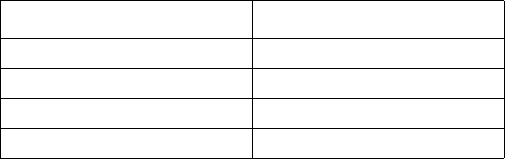
Frames that match the user defined criteria are given a priority tag. The switch supports four
hardware priority levels per egress port, so the eight levels (0-7) of priority are mapped to four
hardware queues (0-3) as listed in the table below.
Note: 0 is the lowest priority, 7 is the highest priority
After an Ethernet frame has been prioritized, the switch forwards the Ethernet frame using the strict
priority-based scheduling algorithm. With this algorithm, any frames residing in a higher priority
queue are always transmitted first. Only when these queues are empty are frames in lower priority
queues transmitted.
It is important to note that this function does not overwrite the existing priority tag on the frame by
default. Instead, the class of service only affects packets inside the switch. The frame retains the
original priority tag value on the egress port.
The switch is capable of overwriting and setting a new priority value in the frame on egress, but
will only do this if User Priority Regeneration is configured on the switch to do so. When User
Priority Regeneration is enabled, the 802.1p priority information that is set for the egress frame is
defined by user.
Prioritization Methods
• MAC Address— Allows frames to be prioritized based on whether the MAC address is:
— Source only
— Destination only
— Source or Destination
• IP Address— Allows packets to be prioritized based on whether the IP address is:
— Source only
Priority in Frames Priority Queue of ASIC
0-1 0
2-3 1
4-5 2
6-7 3
