Radio Interface
5-51
The security mechanisms that may be employed depend on the
level of security required, the network and management
resources available, and the software support provided on
wireless clients. A summary of wireless security considerations is
listed in the following table.
Note: Although a WEP static key is not needed for WEP over 802.1x,
WPA over 802.1x, and WPA PSK modes, you must enable WEP
encryption through the web or CLI in order to enable all types of
encryption in the access point.
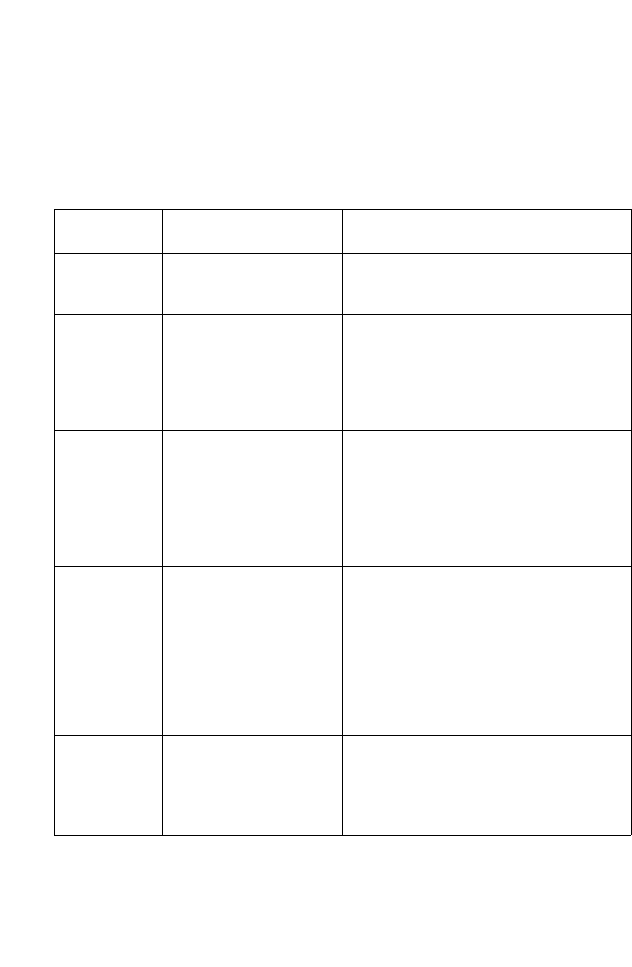
Security
Mechanism
Client
Support
Implementation Considerations
WEP Built-in support on all
802.11a, 802.11b and
802.11g devices
• Provides only weak security
• Requires manual key management
WEP over
802.1x
Requires 802.1x client
support in system or by
add-in software
(native support provided
in Windows XP)
• Provides dynamic key rotation for
improved WEP security
• Requires configured RADIUS server
• 802.1x EAP type may require
management of digital certificates for
clients and server
MAC Address
Filtering
Uses the MAC address
of client network card
• Provides only weak user
authentication
• Management of authorized MAC
addresses
• Can be combined with other methods
for improved security
• Optionally configured RADIUS server
WPA over
802.1x mode
Requires WPA-enabled
system and network
card driver
(native support provided
in Windows XP)
• Provides robust security in WPA-only
mode (i.e., WPA clients only)
• Offers support for legacy WEP clients,
but with increased security risk (i.e.,
WEP authentication keys disabled)
• Requires configured RADIUS server
• 802.1x EAP type may require
management of digital certificates for
clients and server
WPA PSK
mode
Requires WPA-enabled
system and network
card driver
(native support provided
in Windows XP)
• Provides good security in small
networks
• Requires manual management of
pre-shared key


















