Configuring IP Filters and Blocked Protocols
144
2. Enter or select data for each field that applies to your rule.
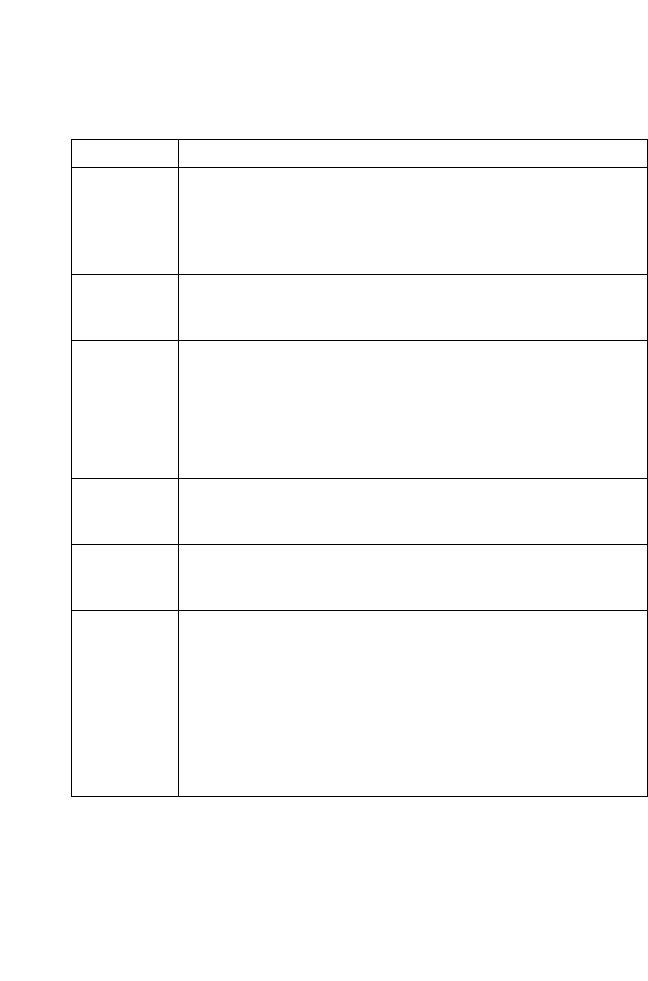
The following table describes the fields:
Field Description
Rule ID: Each rule must be assigned a sequential ID number. Rules are
processed from lowest to highest on each data packet, until a
match is found. It is recommended that you assign rule IDs in
multiples of 5 or 10 (e.g.,
10
,
20
,
30
) so that you leave enough
room between them for inserting a new rule if necessary.
Action: The action that will be taken when a packet matches the rule
criteria. The action can be [Accept] (forward to destination) or
[Deny] (discard the packet).
Direction: This field specifies whether the rule should apply to data packets
that are incoming or outgoing on the selected interface.
[Incoming] refers to packets coming from the LAN.
[Outgoing] refers to packets going to the Internet.
You can use rules that specify the incoming direction to restrict
external computers from accessing your LAN.
Interface: This is the interface on the ADSL Barricade on which the
rule will
take effect. See the examples on page 149 for suggestions
on
choosing the appropriate interface for various rule types.
In Interface: This is the interface from which packets must have been
forwarded to the interface specified in the previous selection.
This option is valid only for the outgoing direction.
Log Option: When [Enable] is selected, a log entry will be created on the
system each time this rule is invoked. The log entry will include
the time of the violation, the source address of the computer
responsible for the violation, the destination IP address, the
protocol being used, the source and destination ports, and the
number violations occurring in the previous x minutes. (Logging
may be helpful when troubleshooting.) This information can also
be e-mailed to designated administrators. See Configuring
Firewall Settings on page 135 for instructions.


















