344 Chapter 20: Number Bases
20NUMBAS.DOC TI-89/TI-92 Plus: Number Bases (English) Susan Gullord Revised: 02/23/01 1:17 PM Printed: 02/23/01 2:19 PM Page 344 of 6
Steps
³
TI
.
89
Keystrokes
›
TI
.
92 Plus
Keystrokes Display
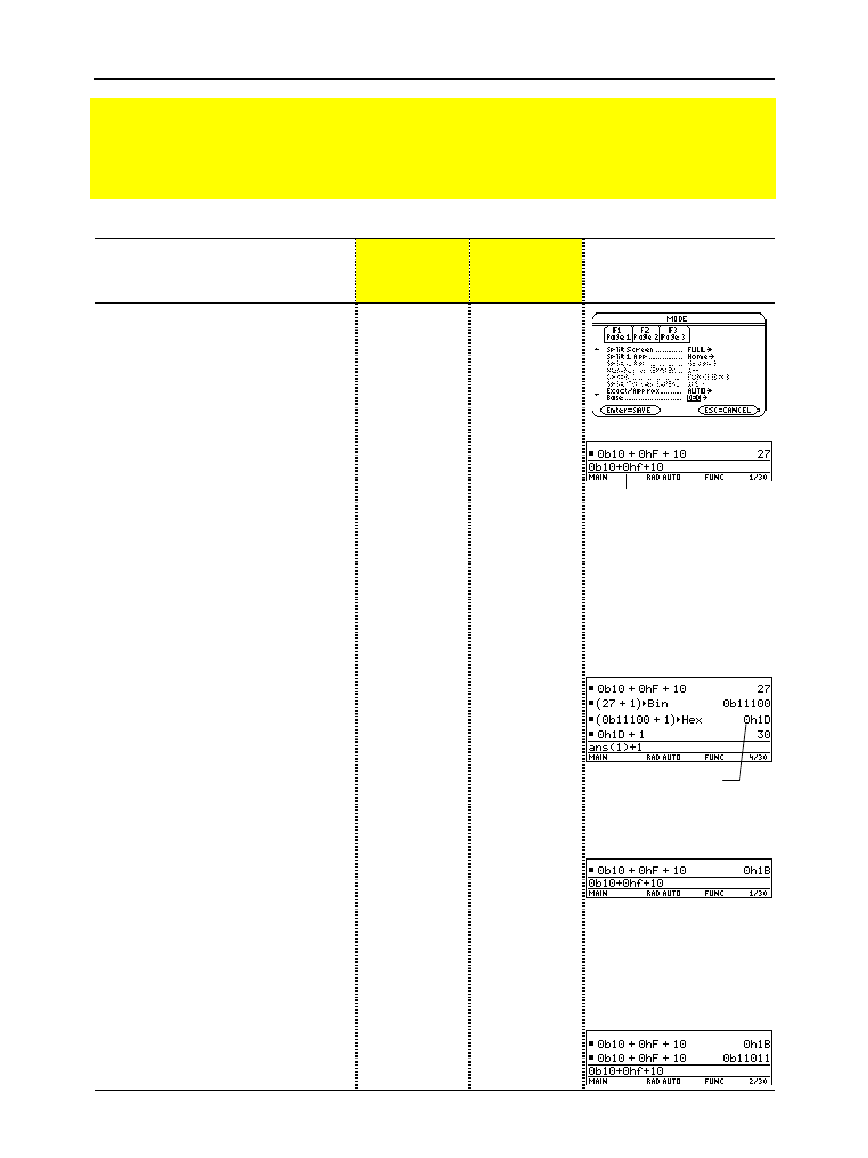
1. Display the
MODE
dialog box,
Page 2. For
Base
mode, select
DEC
as the default number base.
Integer results are displayed
according to the
Base
mode.
Fractional and floating-point results
are always displayed in decimal form.
3„
(use
D
to move
to
Base
mode)
B
1
¸
3„
(use
D
to move
to
Base
mode)
B
1
¸
2. Calculate 0b10+0hF+10.
To enter a binary or hex number, you
must use the
0b
or
0h
prefix (zero and
the letter
B
or
H
). Otherwise, the entry
is treated as a decimal number.
O
j
B10
«
O
2™
HF
j«
10
¸
OB10
«
O
HF
«
10
¸
3. Add 1 to the result and convert it
to binary.
2
displays the
4
conversion operator.
«
1
2
2™
BIN
j¸
«
1
2
BIN
¸
4. Add 1 to the result and convert it
to hexadecimal.
«
1
2
2™
HEX
j¸
«
1
2
HEX
¸
5. Add 1 to the result and leave it in
the default decimal base.
«
1
¸
«
1
¸
6. Change the
Base
mode to
HEX
.
When
Base
=
HEX
or
BIN
, the magnitude
of a result is restricted to certain size
limitations. Refer to page 346.
3„
(use
D
to move
to
Base
mode)
B
2
¸
3„
(use
D
to move
to
Base
mode)
B
2
¸
7. Calculate 0b10+0hF+10.
O
j
B10
«
O
2™
HF
j«
10
¸
OB10
«
O
HF
«
10
¸
8. Change the
Base
mode to
BIN
.
3„
(use
D
to move
to
Base
mode)
B
3
¸
3„
(use
D
to move
to
Base
mode)
B
3
¸
9. Re-enter 0b10+0hF+10.
¸
¸
Preview of Number Bases
Calculate 10 binary (base 2) + F hexadecimal (base 16) + 10 decimal (base 10). Then,
use the
4
operator to convert an integer from one base to another. Finally, see how
changing the Base mode affects the displayed results.
Results use the 0b
or 0h prefix to
identify the base.
Important:
The 0b or 0h
prefix is a zero, not the letter
O, followed by B or H.


















