Chapter 34 Static Route
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
320
34.2 Configuring Static Routing
Click IP Application > Static Routing in the navigation panel to display the
screen as shown.
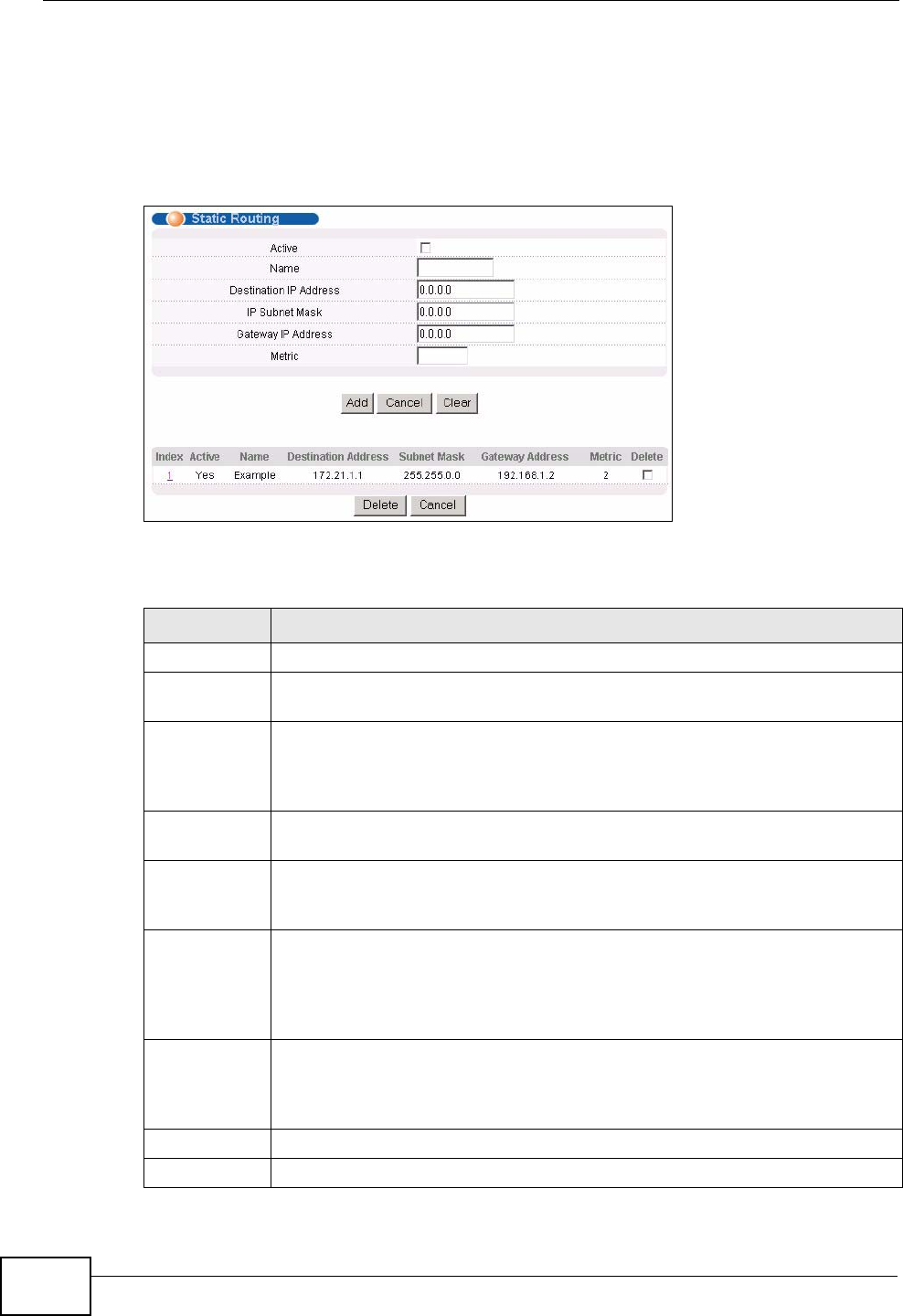
Figure 155 IP Application > Static Routing
The following table describes the related labels you use to create a static route.
Table 108 IP Application > Static Routing
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active This field allows you to activate/deactivate this static route.
Name Enter a descriptive name (up to 10 printable ASCII characters) for
identification purposes.
Destination
IP Address
This parameter specifies the IP network address of the final destination.
Routing is always based on network number. If you need to specify a route
to a single host, use a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255 in the subnet
mask field to force the network number to be identical to the host ID.
IP Subnet
Mask
Enter the subnet mask for this destination.
Gateway IP
Address
Enter the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is an immediate
neighbor of your Switch that will forward the packet to the destination.
The gateway must be a router on the same segment as your Switch.
Metric The metric represents the “cost” of transmission for routing purposes. IP
routing uses hop count as the measurement of cost, with a minimum of 1
for directly connected networks. Enter a number that approximates the
cost for this link. The number need not be precise, but it must be between
1 and 15. In practice, 2 or 3 is usually a good number.
Add Click Add to insert a new static route to the Switch’s run-time memory.
The Switch loses these changes if it is turned off or loses power, so use the
Save link on the top navigation panel to save your changes to the non-
volatile memory when you are done configuring.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Clear Click Clear to set the above fields back to the factory defaults.
