Chapter 43 ARP Learning
XGS-4526/4528F/4728F User’s Guide
382
43.1.2.1 ARP-Reply
By default, the Switch is in ARP-Reply learning mode and updates the ARP table
only with the ARP replies to the ARP requests sent by the Switch. This can help
prevent ARP spoofing.
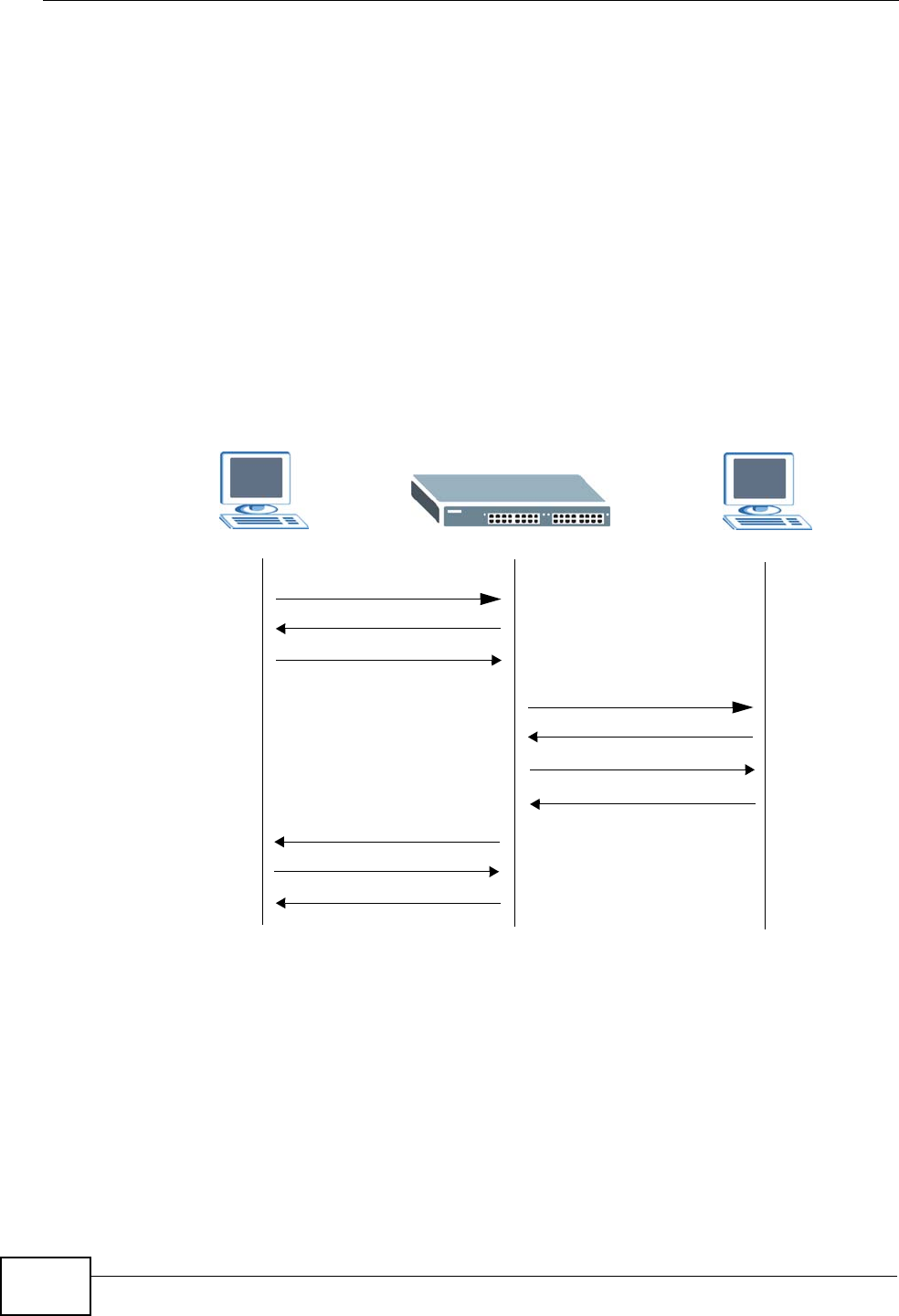
In the following example, the Switch does not have IP address and MAC address
mapping information for hosts A and B in its ARP table, and host A wants to ping
host B. Host A sends an ARP request to the Switch and then sends an ICMP
request after getting the ARP reply from the Switch. The Switch finds no matched
entry for host B in the ARP table and broadcasts the ARP request to all the devices
on the LAN. When the Switch receives the ARP reply from host B, it updates its
ARP table and also forwards host A’s ICMP request to host B. After the Switch gets
the ICMP reply from host B, it sends out an ARP request to get host A’s MAC
address and updates the ARP table with host A’s ARP reply. The Switch then can
forward host B’s ICMP reply to host A.
43.1.2.2 Gratuitous-ARP
A gratuitous ARP is an ARP request in which both the source and destination IP
address fields are set to the IP address of the device that sends this request and
the destination MAC address field is set to the broadcast address. There will be no
reply to a gratuitous ARP request.
A device may send a gratuitous ARP packet to detect IP collisions. If a device
restarts or its MAC address is changed, it can also use gratuitous ARP to inform
A
B
ARP Request
ARP Reply
ICMP Request
ARP Request
ARP Reply
ICMP Request
ICMP Reply
ARP Request
ARP Reply
ICMP Reply


















